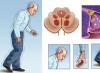
Today, the diagnosis of “cervical erosion” is quite common, in almost every third woman. Erosion is called defects on the surface layer of cells covering the cervix. There are two of its forms: true and false (pseudo-erosion).
Erosion: forms, signs and causes of occurrence
The first form is an ulcer that occurs on the walls of the cervix due to damaged epithelial cells as a result of mechanical action, for example, surgical abortion, traumatic insertion of a tampon, rough sexual intercourse. In the absence of infections and hormonal disorders, such erosion can heal on its own. But the second form, false erosion, is much more dangerous.
It is a response to the formation of cervical defects. In their place, the mucosa begins to grow, as it were, and a large inflamed area forms. Such erosion should be treated to prevent its growth. After all, the places of damage are a very favorable environment for various kinds of infections.
The insidiousness of this disease is that it practically does not manifest itself in any way, especially in the early stages. Sometimes there may be spotting after intercourse or just for no reason in the middle of the cycle. As a rule, women do not pay attention to this, and they learn about the existence of erosion only at a scheduled appointment with a gynecologist. However, the absence of symptoms does not mean that it is worth leaving this fact unattended and postponing treatment. Many nulliparous women do this, because there is an opinion that cauterization can lead to complications during childbirth. Let's see how true this is.

Burn or wait
It is believed that nulliparous women are forbidden to cauterize erosion. The reason for this prohibition is that after the cauterization procedure, a scar remains, which prevents the opening of the cervix during childbirth, as a result of which it begins to stretch poorly and tear. Therefore, all methods of treating erosion in nulliparous women should be excluded, the consequences of which may be:
- scar formation;
- severe damage to soft tissues;
- spontaneous opening of the cervix, which during pregnancy threatens miscarriage.
Until recently, the most common method of treating erosion was cauterization with electricity, which led to all of the above consequences. That is why it does not apply to nulliparous women. But this does not mean that they do not need to treat erosion at all, since postponing therapy can lead to dangerous complications. We are talking about malignant degeneration of the cells of the damaged area.
Cauterization in the traditional sense, of course, is undesirable for the cervix of a nulliparous woman. However, today there are various ways to combat erosion that are suitable for everyone, including those who have not yet become a mother.

Gentle treatments
Treatment of cervical erosion in nulliparous women and girls is carried out only by sparing methods, after which scars and adhesions do not form. To date, there are several such methods. Which one to use, only the doctor decides individually for each patient.
- Medical treatment. This method is appropriate for unstarted erosion, accompanied by inflammatory processes. Such treatment is carried out immediately for both sexual partners. In this case, for the duration of treatment, you should refuse sexual intercourse or be sure to use a condom.
- Cryosurgery or freezing. Treatment consists of applying liquid nitrogen to the affected area. As a result, damaged cells freeze and die. In this case, healthy cells are not affected. The procedure is painless and does not cause bleeding after the procedure. There are no scars on the cervix, it is not deformed.
- laser therapy. The essence of the method is the direct effect of the laser beam on the affected tissue. The laser beam penetrates to the required depth and destroys the affected cells, while not affecting neighboring healthy tissues. Vessels are immediately brewed, so there is a rapid healing, and no traces remain at the site of the wound. The method is highly efficient and safe.
- Cauterization by radio waves. It is carried out using the Surgitron apparatus. The procedure is painless, but bleeding may occur for several days after it. You should abstain from sex for 2-3 weeks. And after 4-5 weeks, visit a gynecologist for a follow-up examination.
- Burning with drugs. Impact on the affected areas and the destruction of diseased cells is possible with the help of drugs such as Solkovagin and Vagotil. The first drug allows you to cope with erosion in one procedure. In the second case, several procedures may be required.
Each method is aimed at destroying the affected cells, however, unlike electrocoagulation, the above methods do not entail undesirable consequences for women who are yet to have pregnancy and childbirth. Often, a small erosion at the initial stage is only observed by a gynecologist before treatment is prescribed.
It should be remembered that there are no universal methods for treating erosion, especially in nulliparous women. Only a doctor can assess its nature and prescribe the most appropriate treatment with minimal consequences for the patient.
In any case, you can not leave the state of the cervix unattended, let the disease take its course. Over time, it progresses and can lead to undesirable dangerous consequences. Therefore, you should regularly visit a gynecologist for a routine examination, even if nothing bothers you.
The cervix connects the internal genital organs with the vaginal canal. Damage to the epithelium of her vaginal area can cause infertility, and the degeneration of epithelial cells leads to the occurrence of a malignant tumor of the uterus. Often a woman does not even know about the existence of pathology. Symptoms of concomitant diseases that caused damage to the epithelium may be disturbing. When examining for ailments or during a preventive examination, the gynecologist detects erosion. It is required to choose the appropriate method of treatment.
Content:
What is cervical erosion
The inner surface of the neck is covered with a mucous membrane. Moreover, the composition of the epithelium in the region of the cervical canal itself and its outer part, which extends into the vagina, is different. The cells of the inner epithelium are cylindrical in shape, and in the outer part they are flat. Erosion is formed when cracks appear on the vaginal part of the canal, into which the cylindrical epithelium from the neighboring area enters. Growing, it narrows and even blocks the opening of the cervix, which leads to infertility. Cancerous degeneration of cells is also possible.
Erosion is often confused with cervical ectopia. Ectopia is a non-hazardous movement of a small part of the cylindrical epithelium into the squamous area. At the same time, at the junction of two layers around the exit from the channel, a bright pink stripe is formed, which is easy to confuse with erosion. Ectopia is called pseudo-erosion.
Is it necessary to treat erosion in nulliparous women
Ectopia often appears in nulliparous young women. It appears as a result of hormonal disorders, inflammatory processes. After the elimination of inflammation and the establishment of a hormonal background, such a violation can pass on its own, the normal state of the epithelium is restored.
Treatment of women, especially nulliparous, from cervical erosion is not required if they are not bothered by any painful symptoms. It is only recommended to undergo regular gynecological examinations in order to prevent complications. Treatment is mandatory in the following cases:
- Simultaneously with ectopia, a woman has a chronic inflammatory disease that is difficult to treat.
- A woman has a papillomavirus or other infection, there are complaints of unusual bloody discharge from the genital tract, pain in the lower abdomen, in the lower back.
- If abundant mucous discharge appears, there are cysts.
- In the presence of cervical dysplasia. Dysplasia occurs due to the fact that the inside of the cervical canal turns outward. This condition often occurs in newborns, but by the time of puberty it goes away on its own. If dysplasia does not disappear, then the cylindrical epithelium remains outside, it can degenerate into cancer. In this case, the pathology requires mandatory treatment, regardless of whether the woman is going to give birth in the future or not.
Warning: A malignant tumor in the vaginal area of the uterus in the initial stage is difficult to distinguish in appearance from erosion, therefore, a regular gynecological examination is not enough to establish an accurate diagnosis, colposcopy is required.
Video: Causes of cervical erosion, the need for treatment
Erosion diagnostics
Erosion is detected during a gynecological examination using mirrors. The area of erosion is distinguished by a brighter color and a granular structure of the epithelium. For a detailed study of the changes and the establishment of their benign or malignant nature, the colposcopy method is used. The colposcope helps to examine the affected area with optical magnification and illumination. This allows you to distinguish real erosion from ectopia, to detect changes characteristic of a cancerous tumor. At the same time, a biopsy of the suspicious area can be taken (a piece of tissue is cut out for this). A smear is also taken to detect infection and study the microflora.
A cytological examination of the affected area is done. To do this, using a spatula and a brush, a scraping is taken from the surface of the neck (the procedure is painless). The material is then examined under a microscope. The composition and nature of the tissues of the affected area are examined. A cervical smear is taken to detect papillomavirus (a common cause of cancer).
The danger of erosion treatment in women without children
In the treatment of erosion, the affected cells are destroyed. This can also damage healthy tissue. When they are mechanically removed by various methods of cauterization, scars remain on the neck, fusion of the canal walls may occur. This leads to infertility.
Due to scarring, the tissue loses its elasticity. During childbirth, this can cause tears in the cervix. Scarring leads to the fact that the cervix during pregnancy spontaneously opens, a miscarriage occurs. Because of the fear of complications during pregnancy and childbirth, nulliparous women sometimes delay treatment for cervical erosion until the baby is born. However, it is up to the doctor to decide what to do after the examination.
Erosion is treated in two ways: cauterization and chemofixation. For cauterization are used:
- liquid nitrogen (cryolysis);
- electricity;
- radio waves;
- laser radiation.
Video: What is ectopia. How to treat erosion in nulliparous women
What methods are used to treat erosion in nulliparous women
Cervical erosion in nulliparous women is most often treated by chemofixation. Preparations are used (Vulstimulin, Vagotil, Solkovagin) containing a mixture of acids. When treating the affected surface, they destroy diseased cells without damaging healthy ones. After treatment, the wound heals quickly without leaving scars.
To cure nulliparous women, the non-contact laser cauterization method and the radio wave method are also used. Their advantage is that healing is much faster than with contact methods. Scars do not form.
For the regeneration of the mucous membrane during erosion in nulliparous women, suppositories (Depantol, Hexicon) are also used for insertion into the vagina. Other methods are used for nulliparous only in case of emergency.
Cervical erosion is a defect in the mucous membrane that occurs for a variety of reasons. Pathology appears at a fairly young age and is often found in nulliparous women. The peak incidence occurs in 20-30 years, that is, at a time when many of the fair sex are seriously thinking about motherhood. Any problem during this period is seen as a potential threat to pregnancy, and erosion is no exception. But is this condition as dangerous as they say?
The issue of possible complications and risks is directly related to the problem of treating cervical erosion in nulliparous women. Contrary to popular belief, it is possible and necessary to treat pathology, but only when there are real indications for this. For the treatment of cervical diseases in women planning a pregnancy, only safe and gentle methods are used. After a well-conducted therapy, it is possible to successfully conceive and bear a child and to give birth independently on time.
Erosion that can be left untreated: myth or reality?
If you take a walk through the numerous Internet forums, you can find very interesting facts about the treatment of cervical pathology. For example, many young women are sure that erosion does not need to be treated. It is believed that the disease that occurred before childbirth is not dangerous, and after the baby is born, it will go away by itself without medical intervention. Is it really?
There is only one form of erosion that does not really require treatment at a young age. We are talking about (pseudo-erosion). In this condition, the cylindrical epithelium of the cervical canal passes to the outer part of the organ. On examination, a pink stain is visible - erosion. Such a defect usually covers the opening of the cervical canal around, but may be located in the form of a small spot only on the upper or lower lip of the cervix.

With ectopia (pseudo-erosion) of the cervix, the cylindrical epithelium is found in the region of the vaginal part of the cervix.
Ectopia that occurs before the age of 25 is considered a variant of the norm. This is not a disease, but only an individual feature of the body. Over time, the columnar epithelium will shift towards the cervical canal without any treatment. Pathology is detected in 40% of all gynecologist patients and is usually detected during the first examination in the mirrors after the onset of sexual activity.
On a note
Bloody discharge after intercourse is one of the main signs of erosion. When such a symptom appears, you should see a doctor.
Uncomplicated cervical ectopia does not require treatment. Regular observation by a gynecologist is recommended (at least 1 time per year), compliance with the rules of personal hygiene. Treatment is carried out only if there are indications:
- A pronounced inflammatory process against the background of ectopia;
- Frequent contact bleeding;
- The combination of ectopia and other pathology (leukoplakia, CIN);
- Identification of atypical cells and suspicion of cervical cancer.
Uncomplicated ectopia resolves on its own after 25 years. Often, erosion disappears soon after the birth of the first child due to changes in hormonal levels.
Erosion to be treated
Not only cervical ectopia is detected in nulliparous women. After the examination, another pathology is often found:
- True erosion is a mucosal defect after a burn, injury or inflammatory process;
- Leukoplakia - keratinization of the mucous layer of the cervix;
- Dysplasia, or CIN - cervical intraepithelial neoplasia;
Against the background of any of these diseases, acute or chronic cervicitis (inflammation of the cervix) can occur. When HPV is infected, papillomas are often detected - specific formations on the skin and mucous membranes.

Inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis) is associated with the activation of pathogenic microorganisms. Without proper treatment, it can lead to deep tissue damage and increase the risk of cervical erosion.
Important point
If any pathology of the cervix is detected, it is necessary to undergo an examination for STIs, including the human papillomavirus.
All diseases of the cervix, except for congenital ectopia, are subject to mandatory treatment. They do not go away on their own, and even a change in the hormonal background after childbirth does not affect their course too much. Deep mucosal lesions (dysplasia II and III) are considered precancerous diseases and pose a real threat to a woman's life. The choice of a specific method of therapy will depend on the form of pathology.
Diagnosis before treatment of pathology
Therapy of diseases of the reproductive sphere is not carried out without preliminary diagnosis. Mandatory examinations include:
- Screening for infections (including HPV and other STIs);
- Colposcopy.

An analysis of the epithelium of the cervix (a smear for oncocytology) is a prerequisite for examining the patient before starting treatment.
According to indications, a biopsy is taken from the mucous membrane of the cervix. Further tactics will depend on the results obtained.
Possible options:
- If uncomplicated cervical ectopia is detected, treatment is not carried out, the girl is recommended to visit a gynecologist every 6–12 months (if complaints appear, you should see a doctor as soon as possible);
- With the development of cervicitis against the background of erosion, the treatment of inflammatory processes is indicated, after which the tests are taken again, the tactics of therapy are revised if necessary;
- In the case of true erosion, its main cause is necessarily eliminated - cervicitis, the consequences of injury or burns;
- When dysplasia, leukoplakia or ectropion is detected, the optimal treatment regimen is selected (drug and destructive methods);
- If cancer is suspected, a woman is referred for a consultation with an oncogynecologist.(Further tactics will depend on the results of the survey).
Modern methods of treatment of cervical erosion in nulliparous women
All therapies must meet the following requirements:
- Efficiency: low percentage of recurrence;
- The ability to capture the entire affected area at once and perform all the manipulations in one go. Sufficient depth of penetration into the mucous membrane;
- Safety: low risk of complications, including bleeding, infection;
- Absence of scars on the cervix after the procedure;
- The ability to take material for a biopsy (important if a malignant tumor is suspected).
Under these conditions, manipulation is considered safe and can be used to treat cervical erosion in women planning a pregnancy. The following methods of therapy meet all these requirements:
Chemical coagulation
The essence of the method: the use of various drugs for direct application to the cervix.
An effective non-contact method that allows you to get rid of the defect on the mucous membrane without damaging healthy tissues. Does not require anesthesia, performed on an outpatient basis. It is considered one of the best ways to treat erosion in women planning a pregnancy.
On a note
After radio wave exposure, no scars remain, the cervix is not damaged, conception, gestation and birth of a child pass without any features.

Radio wave coagulation is carried out by the Surgitron apparatus. During the procedure, the doctor acts on the focus with pathology with high-frequency radio waves. This method is recommended for nulliparous women, as it does not leave scars on the cervix.
Laser coagulation
The essence of the method: cauterization of the pathological focus with a laser beam.
It is used for the treatment of erosion, as well as the removal of warts, cysts and other formations on the cervix. Allows you to accurately remove only the affected tissue, without touching healthy areas. Penetrates to a depth of 3–5 mm, therefore it is not used for deep defects.
Argon plasma ablation
The essence of the method: the effect of argon on the defect of the mucous membrane.
It is a non-contact and improved version of the DEC. Unlike electrocoagulation, it does not leave scars, does not provoke the development of bleeding. Effective for shallow lesions of the mucous membrane (up to 3 mm).
On a note
Numerous positive reviews of modern methods of destructive treatment indicate that laser and radio wave coagulation are the preferred treatment options. Both procedures are painless. Recovery after manipulation takes 3-4 weeks. Reviews indicate that women tolerate these procedures quite well and in the future do not experience problems with the birth of a child.
In modern gynecology, DEC () is not used to treat cervical erosion in nulliparous women. After this procedure, rough scars often remain, which further interferes with the conception and bearing of a child. Natural childbirth after DEC is also not always possible, which significantly limits the use of this method in young girls.
Regarding cryodestruction, gynecologists did not come to a consensus. The use of liquid nitrogen in nulliparous women is possible, but the method has its limitations. Cryotherapy is effective only for shallow mucosal defects, and often the doctor fails to capture the entire affected area. High recurrence rate, long recovery period, discomfort during and after the procedure - all this makes cryodestruction not the most suitable method of therapy for nulliparous women.
Medical treatment as an alternative to cauterization
Gynecologists are in no hurry to cauterize cervical erosion in young women. When the situation allows, the doctor prefers to take expectant tactics. But if regular monitoring is sufficient for uncomplicated ectopia, then in the case of other diseases, special therapy is indispensable. Since most erosion occurs against the background of inflammation, the doctor may prescribe such remedies:
- Antibacterial drugs;
- antifungal agents;
- antiviral drugs;
- Means that stimulate the immune system;
- Drugs that accelerate tissue regeneration.

With erosion that occurred against the background of inflammation, the attending physician will definitely prescribe a medication course of treatment.
The treatment is carried out locally, medications are prescribed in the form. The course of therapy can last up to 2-3 weeks. Be sure to restore the microflora of the vagina with probiotics. Such therapy, as a rule, does not allow to remove the erosion itself, but makes it possible to get rid of the accompanying inflammation, eliminate unpleasant symptoms and reduce the risk of contact bleeding. In the future, the doctor may leave the woman under observation or suggest other methods of influence.
Surgical Treatment: Is Surgery Necessary?
Surgical treatment of erosion in nulliparous women is extremely rare and only for special indications:
- CIN II and III with a high risk of degeneration into cancer;
- Malignant tumor of the cervix;
- Inability to carry out treatment by other methods;
- Erosion in combination with cicatricial deformity of the cervix.
Removal of the pathological focus is carried out in the operating room under general anesthesia. A loop excision or conization of the cervix is performed, depending on the form and severity of the pathological process. After such an operation, the risk of scarring is high, which further leads to the appearance of natural problems during pregnancy and childbirth.

During conization, a cone-shaped section of the cervix with pathology is surgically removed.
It is important to understand: not the size of the erosion is critical when choosing a treatment method. A large defect does not mean a mandatory operation. Small but deep erosions sometimes require more serious intervention than surface formations of considerable size. The final decision is made after a complete examination of the patient, including cytological examination and colposcopy.
Rehabilitation after treatment of cervical erosion
The reproductive health of a young nulliparous girl depends not only on how quickly erosion was detected and treated. Much is determined by the rehabilitation after the procedure. In order for the healing of the mucosa to pass without complications, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Restriction of sexual life until complete healing of the mucous membrane of the cervix. On average, the ban on intimate relationships lasts up to 4 weeks or until the next menstruation. Exact recommendations will be given by the gynecologist after the control examination;
- Ban on sports and heavy physical labor for a month;
- Compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene: regular washing with neutral products, refusal of soap;
- The use of drugs that enhance the regeneration of the mucosa and restore the microflora of the vagina (as prescribed by a doctor).
If pain, burning, spotting and other undesirable symptoms appear after the procedure, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible.

If during rehabilitation after treatment of cervical erosion pain occurs, it is urgent to contact a medical institution.
Practice shows that well-conducted rehabilitation significantly increases the chances of a favorable outcome of the disease. And vice versa, non-compliance with the recommendations of the doctor threatens. Any factors that interfere with the normal healing of the mucosa can provoke the appearance of scars, which in the future will negatively affect the reproductive health of a woman and may interfere with a long-awaited pregnancy.
Complications: what will happen if erosion is not treated?
Is it necessary to treat cervical erosion for a young nulliparous girl? Yes, if there are strong indications for this. Otherwise, the disease will develop according to one of the undesirable scenarios:
- Erosion will grow, capturing all new areas of the mucous membrane, which in the future will lead to the development of complications;
- Frequent inflammatory processes and contact bleeding will interfere with normal life, including in the intimate sphere;
- Some diseases of the cervix can develop into cancer, which will create a direct threat to a woman's life.
Dysplasia II and III, leukoplakia and some other diseases are considered precancerous conditions. The disease can last for years without showing itself. Symptoms of cancer occur already in the later stages of the pathological process. Sometimes, to save a woman's life, the uterus and appendages are removed. Of course, after a radical operation, the desired pregnancy is no longer in question.
Consequences of therapy
What are young women afraid of? The fact that after therapy it will not be possible to conceive, endure and give birth to a child on their own. Unfortunately, such fears in some cases are quite justified. Until recently, serious complications were observed after the use of DEC. After cauterization, scars remained on the cervix, the cervical canal narrowed, which led to serious problems:
- Infertility due to severe stenosis of the cervical canal (spermatozoa could not enter the uterus);
- Isthmic-cervical insufficiency - a pathology in which the cervix opens prematurely, miscarriage or premature birth occurs;
- Anomalies of labor activity - scars do not allow the cervix to open during childbirth, which naturally leads to the need for a caesarean section.
After the advent of radio wave therapy and other progressive techniques, the risk of undesirable consequences for nulliparous women has become minimal. It is impossible to completely exclude the development of complications, and therefore gynecologists are in no hurry to cauterize erosion in young girls without obvious indications. The success of the operation largely depends on the qualifications of the doctor and the equipment at his disposal. A properly conducted rehabilitation period also affects the further reproductive health of a woman.

Qualified treatment of cervical erosion and well-conducted rehabilitation have a positive effect on the ability to become pregnant and give birth to a healthy child.
Planning pregnancy and childbirth against the background of cervical pathology
The main question that worries a woman: is it possible to give birth with erosion? Diseases of the cervix usually do not interfere with the conception of a child. If erosion is not accompanied by scarring and stenosis of the cervical canal, spermatozoa can easily enter the uterine cavity, and fertilization will take place without interference. Difficulties arise only when erosion is combined with other gynecological diseases.
The pathology of the cervix does not interfere with the bearing of the fetus and does not affect its development. During pregnancy, the likelihood of infection of erosion and the appearance of contact bleeding increases, but other problems are not expected. Ectopia of the cervix (pseudo-erosion) can completely disappear after the birth of a child due to the restructuring of the hormonal background.
On a note
If the ectopia has not disappeared within a year after childbirth, you should undergo a second examination by a gynecologist.
Independent childbirth with erosion is possible, but complications are not excluded. In childbirth, a rupture of the cervix may occur, which will provoke an increase in erosion or an eversion of the mucous layer of the cervical canal to the outside. After the birth of a child, it is strongly recommended to be observed by a gynecologist in order to control the state of erosion and not to miss the development of complications.
Does this mean that? Not at all. No one knows how the disease will behave in the face of a changed hormonal background. Gynecologists strongly recommend undergoing treatment before conceiving a child. You can plan pregnancy 2-3 months after cauterization (in the absence of complications).
An interesting video: is it possible to cauterize cervical erosion for a nulliparous woman
Expert opinion: when cervical erosion in a nulliparous woman requires treatment
Cervical erosion is diagnosed in every second woman. Half of them do not know about the disease, since this gynecological pathology in the early stages is asymptomatic. Very often, nulliparous women are at risk.
Untimely therapy can lead to infertility and cause the development of a malignant tumor. In order not to bring the body to a state where the treatment will be long and difficult, it is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist. The doctor detects erosion of the cervix in a nulliparous woman during examination, but in order to establish the cause of the onset of the disease, an additional examination will be required.
The most common causes of cervical erosion in nulliparous patients are hormonal disorders and inflammation in the genital area. If the work of the body and reproductive organs is normalized, the damaged epithelium can recover on its own.
In addition to inflammation and hormonal disruptions, the occurrence of erosion is provoked by:
- sexually transmitted infections;
- injuries during sexual intercourse;
- abortions, miscarriages;
- early sexual life;
- improperly selected contraceptives;
- endocrine diseases;
- weak immunity.
If, in the presence of erosion, a nulliparous woman does not experience pain symptoms, they do not resort to treatment. Very often, signs of erosive damage disappear after the birth of a child. Visits to the doctor in such cases are not canceled, since the identified disease can return at any time. Relapses happen frequently. To avoid the development of complications, visit the gynecologist 1-2 times a year.
Hidden and overt symptoms
Dangerous conditions include large erosions in nulliparous. Such a pathology is accompanied by obvious symptomatics, that is, it is impossible not to notice the problem. The menstrual cycle goes astray, thick discharge is observed, and pains and cramps are regularly felt in the lower abdomen.

The hidden form of erosion in nulliparous girls also has its own signs. It is difficult to recognize them, but with a careful attitude to oneself and atypical manifestations, deviations can be detected. Pay attention to any changes in the body: the appearance of copious whites, an increase in the duration of menstruation, pulling pains in the lower abdomen. If such conditions have not been noted before and become regular, go to the doctor.
Diagnosis and treatment
Nulliparous girls can live with erosion until childbirth, but in some cases it is unsafe. Without treatment, the disease progresses. If the doctor decides to postpone therapeutic measures, the course of the disease must be monitored.
Damage to the uterine mucosa is detected during examination by a gynecologist. The affected area of the epithelium is visible through special mirrors. The erosive ulcer has a bright red color and a granular structure. For a deeper study of the internal defect and erosion testing for good quality, they are carried out. This type of diagnosis makes it possible to detect any changes that are characteristic of malignant tumors.
Mandatory measures during the examination include a biopsy, smears for the study of microflora and the detection of dangerous infections.
Thanks to the emergence of new technologies and drugs, doctors know how to cure cervical erosion in a nulliparous girl effectively and painlessly. Depending on the size and type of pathology, conservative or surgical methods are used.
Conservative therapy
Conservative treatment is considered the safest for eliminating an erosive cervical defect in nulliparous girls. Medicines help to cope with the disease. The doctor may prescribe Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, immunomodulators, Hexicon and Depantol suppositories. Vitamins and tonics are always involved in the elimination of small erosions in nulliparous women.

Chemofixation has proven itself well using preparations that contain a mixture of acids: Vagotil, Vulstimulin,. During the treatment of affected tissues with chemical compounds, diseased cells are destroyed. Healthy tissues are not damaged. There are no scars after the procedure.
Cauterization erosion
When conservative treatment of erosion in nulliparous is ineffective, a surgical operation is prescribed. It is an ordinary burn, with the help of which damaged tissue is simply removed. The difference is only in the way of influence. Before childbirth, radio waves, liquid nitrogen are used. The use of the method of diathermocoagulation (cauterization with electric current) is contraindicated, since subsequently a woman may have problems with childbirth and conception.

Main danger
Erosion treatment allows you to isolate and eliminate damaged parts of the epithelium, but healthy cells can also be affected during the procedures. Radical therapy leads to disruptions in the menstrual cycle and exacerbations of chronic diseases. The greatest danger of erosion treatment is the possible splicing of the canal and rough scars. Atresia of the cervical canal (fusion) often leads to infertility, and the presence of scars and scars negatively affects the structure of tissues. During childbirth, the loss of elasticity causes complications in the form of ruptures.
In addition, scarring often causes the uterus to dilate spontaneously during pregnancy. This may cause a miscarriage.
Congenital ectopia is not considered a pathology. According to experts, this is one of the stages in the formation of the genital organs. Therefore, cervical erosion in virgins is not treated. The same approach is often practiced for nulliparous women. Due to the high risk of complications and serious consequences, doctors do not recommend therapeutic measures before the birth of the first child. But such decisions are made only after a thorough examination. There are critical cases when non-intervention can be dangerous to the health and life of the patient.
Establishing the diagnosis of ectopia during examination by a gynecologist raises the question of treatment for a woman. The doubt whether it is necessary to cauterize erosion is based on a prejudice about the pain and harm of the procedure. Delaying treatment destabilizes the body and may cause difficulties with conception in the future.
The absence of symptoms during cervical erosion does not alarm a woman and she learns about the diagnosis, most often, during a preventive examination by a gynecologist. The doctor in most cases does not detail the patient's condition and the decision on treatment is made intuitively.
Information about whether erosion can be cauterized for nulliparous will allow you to make an informed decision about timely and adequate treatment.
The diagnosis that a gynecologist voices to a woman may imply three different conditions of the mucous membranes of the cervix. It:
- true erosion, in which bleeding wounds and microcracks are found on the cervix, when pressed, drops of blood or ichor are released;
- ectopia, go the appearance of red areas on the cervix. They can be of various sizes and, if severe, cover the entire neck. Red spots are formed by a specific cylindrical epithelium, characteristic of the internal (cervical) canal of the cervix;
- congenital ectopia, which is a feature of the development and formation of the internal genital organs of a woman and is considered a physiological, natural condition that disappears on its own after reaching the age of 20.

Areas of red epithelium on the cervix are formed by cylindrical cells, which are located in one layer. Their functions differ from those that are performed by ordinary cells of the integumentary pink epithelium, tightly interconnected and arranged in several rows.
The cervical epithelium is single-row, unable to protect the cervix from mechanical damage that may occur during intercourse. Normally, the mucous membranes of the cervix and vagina secrete a small amount of liquid mucus, the purpose of which is to remove dead epithelial cells and bacteria.
The purpose of cylindrical cells is different - they must ensure the targeted movement of sperm to the uterus. The thick mucus that they produce hermetically closes the cervical canal, preventing third-party fluids and infections from entering the cervix.
Areas of red epithelium that appeared in the wrong place begin to produce atypical mucus, which becomes a breeding ground for various pathogenic microorganisms, which, under certain conditions, can provoke the appearance of inflammatory processes.
The state of true erosion is diagnosed quite rarely - wounds and injuries are detected within 10-14 days and tend to self-heal. The affected areas, for various reasons, are covered not with a flat, but with a cylindrical epithelium, that is, an ectopia is formed.
Causes of erosion
Many women cannot correlate the fact of the appearance of erosion with the absence of an active sex life or the absence of children. The true causes of erosion are not fully understood, the number of women who show signs of erosion or ectopia allow us to speak of pathology as a complex condition.
The cause of congenital erosion in nulliparous women is the failure of the natural mechanism of maturation of the internal genital organs of the girl. Normally, in female infants, the entire vagina is lined with cervical epithelium. As you grow older and change the hormonal background, the cervical epithelium is replaced by a flat one.
In women with congenital ectopia, the "growing up" of the epithelium is delayed due to a mechanism that has not been fully studied. The condition does not require any treatment. Fears at the doctor can arise only in case of accession of a pathogenic infection.
The causes of erosion in nulliparous women can be:
- infection with sexually transmitted diseases or a specific sexual infection (gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, etc.);
- hormonal disorders due to prolonged use of hormonal contraceptives;
- thyroid disease;
- incorrect or unsuccessful setting of the intrauterine device;
- previous abortions;
- infection with the human papillomavirus and its activation;
- development of a herpetic infection;
- too hard sex;
- use of simulators and mechanical vibrators;
- changes in the vaginal flora under the influence of frequent sexual intercourse with different partners;
- too rare sexual intercourse;
- psychosomatic factors.
Acquired erosion in the early stages of development does not cause concern for a woman. Some small deviations from the norm are perceived as temporary symptoms. The increase in pain during intercourse and the appearance of secretions indicate the attachment of inflammation to existing erosion.
Manifestations of erosion
Symptoms of true erosion can be:
- pain in the lower abdomen after sexual intercourse or before menstruation;
- pain during sex;
- the appearance of pink, brown or spotting, white with streaks of blood after intercourse;
- the appearance of copious discharge with an unpleasant yellow or greenish odor indicates the attachment of an infection and the appearance of inflammation.


Ectopia can manifest similar symptoms, but more mildly. The danger of erosion and ectopia is that they support inflammatory processes in the body, destabilizing its condition.
The growth of the cylindrical and glandular epithelium into cysts can block the access of sperm to the cervical canal and prevent conception.
To correct such conditions, cauterization is used in combination with conservative treatment. This term is not entirely correct, it has been preserved since the use of the method of cauterization of ectopia with an electric current.
Erosion treatment methods
The question of whether it is possible to cauterize erosion for nulliparous girls confronts every patient whom the doctor informs about the need for treatment. Until now, most women believe that it is painful and dangerous.


The reason for the fears is as follows: a dozen years ago, diathermocoagulation (cauterization with high-frequency current) was the main way to stop erosion. This method is still used today because of the simplicity and availability of the equipment, the ability of most doctors in the antenatal clinic to work with it. The specificity of the method is severe pain, the cause of which is the effect of current on the muscles of the cervix, the formation of an extensive burn and scars that deform the organ.
Now the method is not applied to nulliparous. Deformation and scars resulting from cauterization do not allow the neck to stretch to the desired diameter, and become an obstacle in childbirth. Its ruptures additionally injure the woman during childbirth and can cause disturbances in the child.
Modern methods of surgical removal of the cylindrical epithelium allow you to gently and sparingly influence the mucous membranes of the internal genital organs, while maintaining the woman's ability to conceive and normal natural childbearing.
To determine the type of cervical erosion, decide whether it can be cauterized or not, only a doctor can do after a complete diagnosis of the condition.
Is it necessary to cauterize erosion and should it be done before childbirth? The tactics of the doctor may be different and depends on the condition of the particular patient.
If a small erosion is diagnosed without traces of inflammatory processes, the doctor can take the position of dynamic observation. It means:
- examination of a woman every 6 months;
- taking a smear for bacteriological culture;
- blood control for the presence of STDs and HPV.


If no infection is observed, cauterization of the ectopia is not performed. Often a woman's body copes with ectopia on its own after the hormonal levels are leveled. If such a woman becomes pregnant, in most cases, cervical erosion after childbirth disappears on its own without treatment.
What will happen if you do not cauterize the erosion that formed before childbirth against the background of inflammatory processes? The female body during pregnancy becomes more vulnerable to infection. The reason is a natural decrease in the immune threshold for the possibility of bearing a child.
Untreated erosion and inflammation will be a source of constant destabilization of the body, affect the course of pregnancy and the condition of the child. In childbirth, the cervix, weakened by erosion, is poorly stretched, less elastic, and often amenable to tearing.
This explains why timely diagnosis and treatment of erosion should be carried out even before conception - this will ensure normal gestation and childbirth.
Diagnostics
The initial stage of treatment is an accurate diagnosis of the woman's condition and determining the cause of the disease. Only after that, the doctor can choose the exact and correct treatment. For this apply:
- examination of the cervix in the mirrors;
- taking a smear to determine the flora of the vagina;
- blood tests to determine the woman's condition and the presence of a sexually transmitted infection, HIV, HPV;
- hormone analysis;
- Analysis of urine;


Accurate diagnosis of the state of the cervix and possible cellular pathologies is possible only after examining it with the help of a colposcope - an apparatus that allows you to examine the organ under targeted light and multiple magnification. When establishing a large erosion, the doctor can apply both conservative and hardware treatment.
Moxibustion treatment
Why is cauterization becoming one of the most optimal methods of treatment? Conservative therapy is longer and may often be ineffective. Cauterization is a shock for the body, which mobilizes internal resources and helps to eliminate the cylindrical epithelium quickly and with great efficiency.


Cauterization is used as an integral part of complex treatment, which includes:
- medicines for the treatment of inflammation. The composition of drugs is determined after bacterial studies;
- fortifying drugs and vitamins;
- traditional medicine recipes;
- hormonal preparations (if necessary);
- lifestyle changes (regulation of sexual life, refusal of alcohol and smoking, weight loss).
For the treatment of nulliparous women, the latest methods of eliminating ectopic epithelium are used:
- laser vaporization;
- radio wave treatment;
- cryodestruction.


The standard of cauterization is radio wave therapy. It is carried out with the help of special devices Surgitron and Fotek. Its positive aspects are:
- painlessness - the waves “push apart” the cells, minimally injuring the tissues;
- bloodlessness - vessels, when exposed to radio waves, are "soldered";
- the formation of a smooth, clean surface in the ectopia zone instead of a scab, characteristic of other types of exposure to mucous membranes;
- a short rehabilitation period that allows you to plan a pregnancy after 3-4 months from the moment of cauterization.
The disadvantage of the method of radio wave cauterization can only be considered its relatively high cost and availability only in large clinics.
Rehabilitation and re-erosion
The behavior of a woman after cauterization is aimed at creating the most favorable conditions for the healing of the cauterized zone. A woman is prescribed:
- sexual rest;
- sparing diet;
- restorative procedures.
Forbidden:
- heavy physical labor;
- bathing in open reservoirs and pools;
- steam room and hot tub;
- smoking and alcohol;
- use of hygienic tampons;
- wearing synthetic underwear.
With the timely and complete implementation of the doctor's prescriptions, the woman recovers after 60 days and can plan to conceive.
If, after childbirth or after any period of time, repeated erosion is diagnosed, the development factor may be:
- incorrect determination of the cause of erosion;
- incorrect behavior of a woman who does not comply with the doctor's prescription.


Timely detection and treatment of erosion with modern methods will allow a nulliparous woman to become pregnant and give birth to a healthy child without complications.