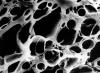
Staphylococcus aureus is a spherical prokaryote, a bacterium of saturated yellow color, outwardly resembles a bunch of grapes, which can be clearly seen in the pictures taken under a microscope.
The microorganism is included in the group of conditionally pathogenic microflora - it is present in a small amount in the body of each person, it begins to actively grow and multiply in the presence of provoking factors. Staphylococcus aureus is a rather tenacious bacterium, tolerates the lack of water, high temperatures, does not immediately die even when boiled, it is not affected by alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, salt, vinegar. But the pathogenic microorganism can be destroyed with the help of ordinary brilliant green.
There is no consensus among doctors about the carriage of staphylococcus, many doctors believe that it is useless to treat it if there are no manifestations of pathology. An exception is pregnant women, expectant mothers need to pass the appropriate tests, if a pathogenic microorganism is detected, urgent treatment will be prescribed.
In children under one year old, Staphylococcus aureus should not normally be in the body.
What it is?
staph infection- the general name for diseases caused by staphylococcus aureus. Due to the high resistance to antibiotics, staphylococcal infections occupy the first place among purulent-inflammatory infectious diseases. Staphylococcus is able to cause an inflammatory process in almost any organ. Staphylococcus can be the cause of purulent diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue: boils, felons, abscesses, hidradenitis, pyoderma. Affecting internal organs, staphylococcus can cause pneumonia, tonsillitis, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, meningitis, abscesses of internal organs. Enterotoxin secreted by staphylococcus can cause severe food intoxication with the development of enterocolitis (inflammation of the small and large intestine).
The genus of staphylococci includes three species: Staphylococcus aureus (the most harmful), Staphylococcus epidermidis (also pathogenic, but much less dangerous than aureus) and Staphylococcus saprophyta - practically harmless, however, also capable of causing diseases. In addition, each of the types of staphylococcus has several subspecies (strains) that differ from each other in various properties (for example, the set of toxins produced) and, accordingly, cause the same diseases that differ in clinic (manifestations). Under a microscope, staphylococci look like clusters of something similar to a bunch of grapes.
Staphylococci are distinguished by a rather high viability: up to 6 months they can be stored in a dried state, do not die during freezing and thawing, and are resistant to direct sunlight.
The pathogenic effect of staphylococci is associated with their ability to produce toxins: exfoliatin, which damages skin cells, leukocidin, which destroys leukocytes, and enterotoxin, which causes a food poisoning clinic. In addition, staphylococcus produces enzymes that protect it from the effects of immune mechanisms and contribute to its preservation and distribution in body tissues.
The source of infection can be a sick person or an asymptomatic carrier, according to some reports, up to 40% of healthy people are carriers of various strains of Staphylococcus aureus. Entrance gates of infection can be microdamages of the skin, mucous membranes of the respiratory tract. A significant factor in the development of staphylococcal infections is the weakening of the immune system against the background of the use of medications (for example, immunosuppressants, antibiotics), chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease), and exposure to adverse environmental factors. Due to the characteristics of the immune system, staphylococcal infections are most severe in young children and old people. Immunity after an infection is unstable and, in general, insignificant, since when meeting with a new subspecies of staphylococcus that produces other toxins, all previous immune “acquisitions” do not carry a significant protective role.
Causes of infection
Staphylococci constantly live on the skin and mucous membranes. Bacteria can enter the body in several ways: contact-household, airborne, alimentary:
- With the contact-household method, the bacterium enters the body through household items. This is the most common route of infection transmission.
- If the carrier of the bacteria coughs, sneezes, then the bacteria are released to the outside along with the air. As a result, when inhaling air contaminated with staphylococci, microorganisms enter the body and, with a decrease in immunity, provoke the development of diseases.
- With the alimentary mechanism of infection, bacteria penetrate through food. Due to non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, microorganisms appear on food. Usually carriers are workers in the food industry.
Pathogenic staphylococcus can enter the body when using insufficiently sterilized medical instruments. The infection enters the body during surgery or when using instrumental diagnostic methods, inserting a catheter, etc. If a pregnant woman has staphylococcus, it is transmitted to the baby.
What diseases are caused by Staphylococcus aureus?
Staphylococcus aureus is capable of infecting most tissues of the human body. In total, there are more than a hundred diseases caused by a staphylococcal infection. Staphylococcal infection is characterized by the presence of many different mechanisms, routes and factors of transmission.
Staphylococcus aureus can very easily penetrate through minor damage to the skin and mucous membranes into the body. Staphylococcal infection can lead to various diseases - ranging from acne (acne) to peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum), endocarditis (inflammation of the inner lining of the heart) and sepsis, which is characterized by mortality in the region of 80%. In most cases, a staphylococcal infection develops against the background of a decrease in local or general immunity, for example, after an acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI).
Community-acquired pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus is rarely recorded, but in inpatient departments it is this type of pathogenic staphylococcus that ranks second in importance among all pathogens (Pseudomonas aeruginosa is in first place). Nosocomial or nosocomial infections can occur due to the penetration of Staphylococcus aureus through various catheters or from wound lesions of the skin into the body.
Staphylococcus aureus is the main causative agent of infections of the musculoskeletal system. This pathogenic bacterium in 75% of cases causes septic (infectious) arthritis in children and adolescents.
Staphylococcus aureus can cause the following diseases:
- rhinitis;
- sinusitis;
- pharyngitis;
- laryngitis;
- bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- osteomyelitis;
- food poisoning;
- pyoderma;
- scalded baby syndrome.
Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus
The specific clinical manifestations of staphylococcal infection depend on the site of introduction of the microorganism and the degree of reduced immunity in the patient. For example, in some people, infection ends with a simple boil, and in debilitated patients, with an abscess and phlegmon, etc.
Common symptoms characteristic of Staphylococcus aureus in adults:
- fast fatiguability;
- general weakness;
- lack of appetite;
- aches in bones and joints;
- nausea and vomiting;
- increase in body temperature.
These are common signs of infection with harmful bacteria. Depending on the strength of the immune system and the resistance of the body systems, this list may be supplemented by other symptoms that more specifically indicate the type of disease.
Damage to the skin
Infections of the skin are characterized by rashes on the skin, the appearance of vesicles with purulent contents, crusts, redness, and seals.
Infections of the ENT organs and eyes
Getting on the mucous epithelium of the throat or nose, staphylococcal infection provokes the occurrence of tonsillitis, otitis media, sinusitis and other inflammatory pathologies of the upper respiratory tract or upper respiratory tract.
When the lungs are affected by Staphylococcus aureus, staphylococcal pneumonia develops, characterized by the appearance of shortness of breath and chest pain, severe intoxication of the body and the formation of many purulent formations in the lung tissues, gradually transforming into abscesses. With the breakthrough of abscesses into the pleural cavity, suppuration of the pleura (empyema) develops.
With damage to the mucous membrane of the eyes, conjunctivitis develops (photophobia, lacrimation, swelling of the eyelids, purulent discharge from the eyes).
Staphylococcus aureus affects the genitourinary system
Urinary tract infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus is characterized by:
- urination disorder (increased frequency, soreness),
- a slight fever (sometimes it may be absent),
- the presence of pus, blood impurities and the detection of Staphylococcus aureus in the general and bacteriological examination of urine.
Without treatment, staphylococcus aureus can infect surrounding tissues (prostate gland, perirenal tissue) and cause pyelonephritis or form kidney abscesses.
CNS lesion
If Staphylococcus aureus enters the brain, it is likely to develop meningitis or a brain abscess. In children, these pathologies are extremely difficult and cases of death are not uncommon. Typical symptoms:
- intoxication syndrome;
- hyperthermia;
- severe vomiting;
- positive meningeal symptoms;
- rash appears on the skin.
food poisoning
It develops when eating contaminated or spoiled food and proceeds with symptoms of acute enterocolitis. Characterized by fever, nausea, vomiting up to 10 or more times a day, loose stools mixed with greens.
Staphylococcus aureus is a dangerous type of bacteria that causes many infections when the patient's immune system is weakened. If you find the first general symptoms (lethargy, nausea, lack of appetite), you should immediately consult a doctor.
The defeat of the musculoskeletal system
This pathogen is the leading cause of purulent lesions of the musculoskeletal system (osteomyelitis and arthritis). Such pathological conditions develop more often in adolescents. In adults, staphylococcal arthritis often develops against the background of existing rheumatism or after joint replacement.
Why is Staphylococcus aureus dangerous?
Normally, Staphylococcus aureus lives on the skin and mucous membranes in almost all people. But healthy people with good immunity do not suffer from staphylococcal infections, since the normal microflora inhibits the growth of staphylococcus and does not allow its pathogenic essence to manifest itself. But when the body's defenses are weakened, the microbe "raises its head" and causes various diseases, up to blood poisoning or sepsis.
The high pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus is associated with three factors.
- Firstly, the microorganism is highly resistant to antiseptics and environmental factors (withstands boiling for 10 minutes, drying, freezing, ethyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, with the exception of "brilliant green").
- Secondly, Staphylococcus aureus produces the enzymes penicillinase and lidase, which makes it protected from almost all antibiotics of the penicillin series and helps to melt the skin, including sweat glands, and penetrate deep into the body.
- And thirdly, the microbe produces endotoxin, which leads to both food poisoning and the syndrome of general intoxication of the body, up to the development of infectious-toxic shock.
And, of course, it should be noted that there is no immunity to Staphylococcus aureus, and a person who has had a staphylococcal infection can become infected with it again.
Staphylococcus aureus is especially dangerous for infants in the hospital. It is in hospitals that the concentration of this microbe in the environment is high, which attaches great importance to the violation of the rules of asepsis and sterilization of instruments and the carriage of staphylococcus among honey. personnel.
When is specific treatment needed?
Taking into account the peculiarities of the coexistence of the human body and Staphylococcus aureus, we can draw the following conclusion regarding the treatment of staphylococcal infections: it is necessary to treat staphylococcus only when a person has real symptoms of the disease, that is, an infection with specific manifestations. In this case, the patient is shown antibiotic therapy.
In all other situations, for example, when carrying Staphylococcus aureus in the respiratory tract or intestines, it is necessary to take measures to increase local and general immunity so that the body gradually clears itself of the unwanted "neighbor". In addition, medicines are used for sanitation:
- staphylococcal bacteriophage (staphylococcal virus).
- Chlorophyllipt (eucalyptus leaf extract) in various forms of release. If Staphylococcus aureus is detected in the throat, an alcohol solution of Chlorophyllipt diluted with water is used, as well as spray and tablets. To sanitize the nose, an oily solution of the agent is instilled into each nasal passage, and when carried in the intestines, alcohol Chlorophyllipt is used orally.
- ointment Bactroban with the carriage of staphylococcus aureus in the nose.
Treatment of Staphylococcus aureus
In order to get rid of the bacteria, a competent selection of antibacterial therapy is necessary.
The most commonly used treatments are:
- Amoxicillin, which is able to suppress the reproduction and growth of pathogenic bacteria, contribute to their destruction. It has a fairly wide spectrum of action and blocks the production of peptidoglycan. Used with or without food, no more than 1 g three times a day;
- Cephalexin. The drug does not allow the synthesis of components that make up the bacterial cell wall. It must be taken before meals, every 6 hours;
- Cephalotin, which disrupts the ability of bacteria to divide normally, and also has a destructive effect on the membrane of staphylococci. Used both intravenously and intramuscularly;
- Cefotaxime. The drug is aimed at suppressing the growth of bacteria, does not allow them to multiply. Apply both intravenously and intramuscularly. The dosage is selected individually;
- Vancomycin, promotes blocking of a component that is part of the bacterial cell membrane, changes the degree of permeability of its wall, which leads to the death of staphylococcus aureus. Given intravenously, either every 6 or every 12 hours. The dosage is determined by the doctor;
- Cloxacillin. Contributes to the blocking of membranes that are at the stage of bacterial division. It is necessary to take the drug every 6 hours at a dosage of 500 mg;
- Cefazolin. It has a wide spectrum of action, does not allow the components of the bacterial cell wall to be produced. Can be used both intravenously and intramuscularly, up to 4 times a day;
- Oxacillin. It has a detrimental effect in the later stages of bacterial development and contributes to their destruction. Used intravenously, intramuscularly and orally;
- Clarithromycin, which prevents bacteria from making their own proteins. It is most commonly used in tablet form, although it may be given intravenously for severe infections;
- Erythromycin also interferes with protein production, must be applied every 6 hours;
- Clindamycin is also aimed at eliminating the ability of bacteria to produce a certain protein, which leads to its death.
Before starting to use this or that remedy, it is necessary to conduct an antibiogram. This will help to identify the sensitivity of staphylococcus to a particular drug. Conducting such a study is relevant for the health of the patient, this will guarantee that the bacterium does not develop resistance.
Any antibacterial agents can be prescribed exclusively by the attending doctor and only after a thorough diagnosis.
Treatment of staphylococcal infection requires strict adherence to the frequency of administration, the time of use of the drug and its dosage. It is important to take the prescribed antibiotic not until the first symptoms disappear, and not less than 5 days. If it is necessary to extend the course, the doctor will inform about it. In addition, you can not stop treatment, therapy must be continuous.
Antibiotic resistance
Since the discovery of penicillin and its active use against staphylococcus, under the pressure of natural selection, a mutation has been fixed in the population, due to which most strains are currently resistant to this antibiotic, due to the presence of penicillinase in Staphylococcus aureus, an enzyme that breaks down the penicillin molecule.
To combat the bacterium, methicillin is widely used - a chemically modified penicillin that penicillinase does not destroy. But now there are strains that are also resistant to methicillin, and therefore strains of Staphylococcus aureus are divided into methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), even more resistant strains are also distinguished: vancomycin-resistant (VRSA) and glycopeptide-resistant (GISA).
The bacterium has about 2600 genes and 2.8 million base pairs of DNA in its chromosome, which is 0.5-1.0 µm long.
For the treatment of staphylococcus, a staphylococcal bacteriophage is used - the drug is a liquid medium in which there are phage viruses that destroy staphylococci.
In 2008, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) established an active, pronounced inhibitory effect on methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus aureus of copper and copper alloy surfaces.
Surgery
Skin and soft tissue infections
Of paramount importance is the drainage of all purulent foci. For small abscesses without fever in children, drainage alone may be sufficient, as antibiotic treatment may be equivalent to adequate drainage. Subcutaneous drainage has been proven to be more effective than incision and drainage.
Osteomyelitis
Surgical treatment is usually indicated to remove purulent contents from the subperiosteal space or in the presence of an infected foreign body.
Septic arthritis
In younger children, septic arthritis of the hip or shoulder is an indication for emergency surgery. Joints should be drained as soon as possible to prevent bone destruction. If adequate drainage with a needle preceded, but there is a large amount of fibrin, destroyed tissues, then surgical intervention is also necessary.
Endocarditis
If endocarditis is associated with a foreign body, then its removal is necessary.
toxic shock syndrome
All potential foci of infection should be identified and drained.
Thrombophlebitis
Remove an infected intravenous device in immunocompromised or critically ill patients when the infection cannot be controlled medically.
Diet and nutrition
With a staphylococcal infection, it is important not only to suppress the activity of the pathogen, but also to increase immunity. Diet is important in this process. The main role in the opposition to staphylococcus is given to lysozyme. With its lack, it will be difficult to get rid of the pathology.
The diet should be diversified with food rich in vitamins, protein and carbohydrates. Fiber is also essential as it helps to flush out toxins from the body. The menu is made up of the following products:
- Proteins (meat, poultry, cheese, cottage cheese, fish).
- Carbohydrates (buckwheat, potatoes, durum pasta, wheat).
- Fiber (raw and baked vegetables).
- Vegetable proteins (nuts, lentils, beans).
- Vegetable fats.
The consumption of salt, spices and fats of animal origin is reduced as much as possible.
Prevention
To avoid staphylococcal infection, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system - eat right, exercise regularly, take vitamin complexes, get rid of addictions, do not forget about hardening and daily walks in the fresh air.
Basic Precautions:
- get vaccinated against staphylococcus in a timely manner;
- observe hygiene rules, wash hands and face often and thoroughly;
- wash all vegetables and fruits thoroughly;
- buy dairy, meat products only in trusted places, study the terms and conditions of storage on the label;
- do not eat food on the street;
- even minor scratches should be immediately treated with antiseptic solutions;
- do not use other people's toiletries and bedding.
Any contact with people who have signs of a staph infection should be avoided. It is better for women to be tested for the presence of pathogenic bacteria at the stage of pregnancy planning in order to prevent the risk of infection of the child.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the location of the pathological focus of staphylococcal infection, the severity of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment.
With mild lesions of the skin and mucous membranes, the prognosis is almost always favorable. With the development of bacteremia with damage to internal organs, the prognosis deteriorates sharply, since in more than half of the cases such conditions end in death.
- This is a bacterium that has the correct spherical shape and belongs to the group of gram-positive non-motile cocci. For humans, staphylococcus in some cases is part of the conditionally pathogenic microflora, that is, it always lives on the body. But pathogenic staphylococcus is also isolated, which, once inside the body, will definitely cause a disease. In addition, the pathogen is widely distributed in nature.In the presence of certain conditions conducive to this, the bacterium can exhibit pathological activity and cause an inflammatory process in any organ or group of organs. It can be skin, nervous tissue, brain, heart, digestive system, etc.
Staphylococcus has a large number of strains (27), the most common and pathogenic of which are golden, epidermal, saprophytic and hemolytic staphylococci. Each of them has a different degree of aggressiveness and pathogenetic activity.
The danger of these microorganisms is that they produce toxins and enzymes that are pathogenic for cells and disrupt their vital functions. Bacteria have a destructive effect on connective tissues, skin and subcutaneous tissue. They cause a number of dangerous diseases, including sepsis, disorders of the central nervous system, pneumonia, purulent skin lesions, general intoxication of the body. Often it is with staphylococcal infection that complications after inflammatory diseases and surgical operations are associated.
Staphylococci are stable in the environment and have a fairly high resistance to antibiotics.
Types of staphylococcus
There are three types of staphylococcus, which are the most common and harmful to the human body:
Saprophytic staphylococcus aureus most often affects women, causing them to have inflammatory diseases of the bladder (cystitis) and kidneys. Saprophytic staphylococcus bacteria are localized in the layers of the skin of the genitals and the mucous membrane of the urethra. Of all the types of staphylococcus, it causes the least lesions;
Epidermal staphylococcus aureus can live on all mucous membranes and any part of the human skin. With normal immunity, the body copes with this bacterium, and it does not cause any disease. But if somehow epidermal staphylococcus aureus gets from the skin into the blood of a person with weak immunity (after a surgical operation), inflammation of the endocardium (the inner lining of the heart) may develop due to blood poisoning;
Staphylococcus aureus is the most common and dangerous type. Adults and children, men and women are equally susceptible to infection. The bacterium can affect any organs, provoking inflammatory diseases, the number of which exceeds a hundred. It is an extremely resistant and tenacious microorganism that can withstand very high temperatures, exposure to direct sunlight, 100% ethyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide and a number of antibiotics. Staphylococcus aureus causes purulent skin lesions (, etc.). It also causes a large number of dangerous systemic and general infections: staphylococcal sepsis, toxic shock, abscess formation in the brain, heart, liver and kidneys, food poisoning, etc.
Staphylococcus symptoms
Symptoms of staphylococcus will depend on which organ or system has been affected. The severity of manifestations is affected by the aggression of the microorganism and the state of immunity of a particular person.
Among the most common diseases caused by staphylococcus, the following can be distinguished:
Pyoderma. As a result of the introduction of bacteria under the skin, a purulent inflammatory process occurs. This can affect the sebaceous and sweat glands, as well as hair follicles. Among the most frequent manifestations of pyoderma, there are folliculitis (inflammation of the upper part of the hair follicle), hydradenitis (when the site of infection is the sweat glands), (when the skin, subcutaneous tissue and a group of hair follicles become inflamed), furuncle (the hair follicle suppurates, sebaceous gland and connective tissues around). Wherever the inflammatory process is localized, it is always accompanied by the appearance of purulent masses, swelling, hyperemia of the surrounding tissues and painful sensations of varying intensity. In some cases, nausea can also occur (more often with carbuncles and hydradenitis);
Rhinitis. Causing an inflammatory process in the nasal mucosa, the bacterium leads to an abundant secretion of mucus, which makes nasal breathing difficult. It is here that the most dangerous type of bacteria most often settles - Staphylococcus aureus. In this case, a person can be both a permanent and temporary carrier. Most often, the patient complains of the following symptoms: shortness of breath, impaired sense of smell, increased secretion of mucous secretion, change in voice timbre, breathing through the mouth. At the beginning there is little mucus, but as the disease progresses, the volume of discharge from the nose increases and they become purulent;
Sinusitis. They are characterized by an inflammatory process localized in the paranasal sinuses. More often than others, the maxillary and frontal regions suffer, which leads to the development of diseases such as or. The disease is very common in the practice of otolaryngologists. Up to 10% of all diseases of the upper respiratory tract in adults are caused by sinusitis. Patients present the following complaints: the impossibility of nasal breathing, rhinophony (nasal), expressed with yellow-green discharge, general weakness, sleep disturbance, lack of appetite, fever (sometimes to high values), pain with localization in the inflamed sinuses. If the infection is acute, then the thermometer shows numbers up to 39 ° C, if it goes into the chronic stage, then no more than 37.5 ° C;
Pharyngitis. They are characterized by an inflammatory process localized in the region of the mucous membrane lining the pharynx. Often, the infection captures nearby tissues of the tonsils. In this case, the disease is called tonsillopharyngitis. Patients experience the following symptoms: redness of the posterior pharyngeal wall, the appearance of viscous mucus on it, a feeling of sore throat, dry, hoarseness, pain when swallowing. All these signs are observed against the background of general weakness, with elevated body temperature and a decrease in appetite. According to statistics, pharyngitis caused by staphylococci is diagnosed in adults in no more than 5% of cases;
Laryngitis. Accompanied by the presence of an inflammatory process in the mucous membrane lining the larynx. Often the trachea is exposed to infection, then the disease is called "laryngotracheitis". A distinctive feature of a staphylococcal infection is the presence of a purulent discharge. In addition, the patient complains of pain in the larynx, dryness and itching, a change in the timbre of the voice, up to its loss. In addition, there is a low body temperature, usually not exceeding 37 ° C;
Bronchitis. The disease is characterized by inflammation in the bronchi. Most often, it begins with the development of a pathological process in the upper respiratory tract with a gradual transition to the larynx, trachea and bronchi. The patient suffers from a cough, which can be both dry and wet with sputum discharge. If the bronchi are affected, the separated sputum will be with purulent contents. In addition, there is an increase in body temperature up to 39 ° C, shortness of breath and pain in the chest;
Pneumonia. When the lung tissue is affected by a staphylococcal infection, the disease has a severe course. Statistics indicate that outside the hospital, a person can get this type of pneumonia in only 1% of cases, but inside the hospital, staphylococcus aureus affects the lungs much more often, on average, in 15% of cases. Among the complex of symptoms there are regular repeated increases in body temperature. That is, it periodically rises and falls, which manifests itself in the form of chills. The patient suffers from severe shortness of breath, muscle weakness, pain when coughing and even when breathing. The place of localization of painful sensations is the chest, they are associated with stretching of the pleura. Sputum is not just mucous, but with purulent impurities. The complexion becomes cyanotic, which is a consequence of oxygen starvation. Often it is staphylococcal pneumonia that leads to the development and empyema of the pleura. The most formidable complication is sepsis;
Osteomyelitis. It manifests itself in purulent-necrotic lesions of bone tissue and bone marrow, as well as soft tissues surrounding the joints. In adulthood, the spine most often becomes inflamed, while the route of infection is hematogenous, that is, the bacterium reaches its destination through the bloodstream. In this case, the symptoms are not too pronounced. The temperature, as a rule, does not exceed subfebrile marks, while the person experiences pain at the site of inflammation and impaired motor function in the joints or back;
Food poisoning, provoked by staphylococcus, develops acutely. Often, the first signs of infection are observed already half an hour after eating contaminated foods. Among the symptoms, patients note abdominal pain, frequent vomiting, and a feeling of nausea.
However, in order for the clinical picture of staphylococcal infections to be complete, it is necessary to give the general symptoms caused by the microorganism:
Local increase in body temperature. It is a local increase in temperature due to the fact that in this way the body tries to cope with a pathogenic bacterium and prevent its reproduction. This method of protection is called bacteriostatic effect;
Hyperemia, which is formed due to a rush of blood to the site of inflammation. In this case, the vessels dilate, and the outflow of venous blood decreases. This is also a protective reaction of the body to infection. In this way, he tries to increase the flow of oxygen in order to neutralize the toxic effect;
Swelling of tissues due to increased vascular permeability;
Painful sensations caused by compression of nerve endings by edematous tissues. Damage to the vessel may also occur due to excessive blood flow, which contributes to the appearance of painful sensations;
Violation of the functionality of organs and tissues as a result of their damage at the cellular level.
It is important not to apply knowledge about the symptoms of staphylococcal infections in adulthood to children. This is due to the fact that the signs of the disease will be slightly different at different ages. This is especially true for newborns and children under one year old.
How is staphylococcus transmitted? Causes of infection
All diseases that a bacterium causes can occur as a result of the fact that the infection enters the body due to a violation of the integrity of the skin or mucous membranes, because it is a permanent inhabitant of the human microflora. In addition, infection can occur exogenously, that is, with food or as a result of close contact.
At the same time, one should not forget that some people are permanent or temporary carriers of this bacterium, which also has a significant role in the possibility of transmission. At the same time, pathogenic bacteria do not manifest themselves in any way, and such people pose a particular danger precisely to those around them.
There are the following possible ways of transmission of infection:
Contact-household way. When bacteria enter the body through various household items or through direct contact with the skin. Sometimes it is enough to use someone else's towel or bedding for infection to occur. In this case, the bacterium can cause both an inflammatory process, and simply infiltrate the body and lead to carriage;
Airborne route. That is, a person inhales the air in which bacteria are present. Most often, sick people become the source of infection, releasing bacteria when coughing, sneezing and just breathing;
Dust. Bacteria tend to exist for a long time in the surrounding dust. When it enters the respiratory tract, infection occurs. This path is called "air-dust";
fecal-oral route, which is also called alimentary. In this case, the release of bacteria occurs during vomiting or defecation of an infected organism. An uninfected person consumes foods containing staphylococcus aureus and becomes ill. Often this happens with insufficient hygiene, namely through dirty hands;
Medical instruments. The bacterium can penetrate into a healthy body through poorly processed medical instruments, this is the so-called artificial method of infection. Infection occurs during the passage of diagnostic procedures, for example, during bronchoscopy, as well as during surgery. An additional danger is that instruments can be disinfected in the usual way, but they contain a bacterium that has developed resistance to specific sanitization methods.
In addition to the listed routes of infection, there are also indirect causes that provoke human infection with staphylococcus aureus:
Any disease that causes a decrease in immune forces. This also includes frequent and severe stress and irregular sleep;
General hypothermia of the body. This cause plays a leading role in the development of the inflammatory process in the upper respiratory tract. At low body temperatures, the work of the cilia of the ciliated epithelium, which line the nasal mucosa, slows down. Thus, it is much easier for staphylococcus to get into the body and provoke an inflammatory process;
Any chronic illness;
Age. According to statistics, newborns, children of early preschool age and the elderly are most susceptible to infection;
Viral infections often precede the disease becoming bacterial. In most cases, this is observed with ARVI, when, against the background of a decrease in immunity, staphylococci existing in the body begin to show pathological activity;
Prolonged use of vasoconstrictor drops that violate the integrity of the nasal mucosa and contribute to the penetration of infection;
Inhalation of allergens and toxic substances leads to bronchial trauma, which can become a provoking factor in the development of bacterial inflammation;
Insufficient hygiene;
Eating contaminated foods;
Violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes or skin.
Degrees of defeat by staphylococcus aureus
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish four degrees of infection with staphylococcus aureus, each of which is characterized by a certain severity and requires different treatment. It is necessary to distinguish between staphylococci, which are unconditionally pathogenic, which are detrimental to blood cells, and opportunistic, which contribute to the development of a minor inflammatory reaction. In addition, there are also saprophytes that cause almost no lesions.
It is the knowledge of the degree of pathogenesis that helps doctors to more accurately select the treatment and predict the nature of the course of the disease. Although the division by degree is very conditional, and in many respects the prognosis depends on the level of immunity of an infected person, as well as on his resistance to bacteria.
A doctor can determine the degree of activity of staphylococcus aureus by taking blood or other biological materials for a laboratory test. He also decides on the need for treatment and the nature of future therapy.
1 degree of damage to staphylococcus aureus
If immunity is normal, then this degree of staphylococcal damage cannot cause pathological processes, which means that treatment is not required. But preventive sanitation of the skin and mucous membranes will not hurt.
2nd degree of staphylococcus aureus
When staphylococcus is found in such a low diagnostic titer, most often doctors do not prescribe treatment. However, a comprehensive examination for the detection of other infections is necessary. This is especially true in the presence of any complaints about the pathological processes occurring in the body.
If it is found that a person has a concomitant infection, then the presence of staphylococcus in the body should be reduced as much as possible with the help of general antibiotic therapy and local sanitation. However, the need for treatment is determined by the doctor and depends on each individual case.
3 degree of damage to staphylococcus aureus
When a person is found to have a grade 3 infection, most physicians agree that antibiotic therapy is necessary. Although in a normal state of immune forces, the bacterium will not be able to provoke an infectious process. Such a degree is considered tolerably possible, but with any failures in the body, it can lead to serious inflammatory reactions.
First of all, the doctor prescribes a treatment aimed at strengthening, if it does not give an effect after 2 months, then a further therapeutic regimen is developed in each case individually.
4 degree of damage to staphylococcus aureus
When grade 4 infection is detected, specific treatment is required, although such indicators are considered only potentially dangerous. It is important to prevent the emergence of antibiotic resistance in bacteria, and it is also necessary to determine the sensitivity of a particular bacterium to a particular agent. Only after this can treatment begin, which in the vast majority of cases (if there are no signs of inflammation) comes down to increasing immunity, getting rid of and.
Complications and consequences of staphylococcus aureus - what will happen if not treated?
When antibiotic therapy is not started in a timely manner, it threatens with serious complications:
Endocarditis. In this case, the heart valves and the inner layers of the heart are affected. At the same time, the patient experiences an increase in heart rate, a decrease in efficiency, and sometimes the body temperature rises. This pathology, in turn, is accompanied by no less serious diseases, among which, etc.;
Meningitiscaused by staphylococcus aureus is characterized by purulent inflammation of the meninges, accompanied by high body temperature, severe nausea and vomiting. At the same time, even timely therapy is not a guarantee that the patient will avoid death. Mortality with adequate treatment is up to 30%;
toxic shock syndrome often referred to as a symptom of a staph infection, but it is a complication of the disease. It consists in a shock reaction of the body in response to infection. In this case, drug therapy is difficult. The patient suffers from elevated body temperature, up to 40 °C, repeated vomiting and diarrhea. , high probability of death;
Blood poisoning is another formidable complication of an untreated staph infection. It occurs when a bacterium enters the bloodstream and begins to poison the body with the produced toxins. It is sepsis caused by staphylococcus aureus that is the most common type of blood poisoning, and also the most dangerous. In addition to extremely high body temperature, he is accompanied by severe headaches, nausea and vomiting, damage to the liver, intestines, lungs, and brain. At the same time, antibiotic therapy without prior antibiogram often leads to high mortality among sick people.
Treatment of staphylococcus
In order to get rid of the bacteria, a competent selection of antibacterial therapy is necessary.
The most commonly used treatments are:
Amoxicillin, which is able to suppress the reproduction and growth of pathogenic bacteria, contribute to their destruction. It has a fairly wide spectrum of action and blocks the production of peptidoglycan. Used with or without food, no more than 1 g three times a day;
Vancomycin, promotes blocking of a component that is part of the bacterial cell membrane, changes the degree of permeability of its wall, which leads to the death of staphylococcus aureus. Given intravenously, either every 6 or every 12 hours. The dosage is determined by the doctor;
Cloxacillin. Contributes to the blocking of membranes that are at the stage of bacterial division. It is necessary to take the drug every 6 hours at a dosage of 500 mg;
Cefazolin. It has a wide spectrum of action, does not allow the components of the bacterial cell wall to be produced. Can be used both intravenously and intramuscularly, up to 4 times a day;
Oxacillin. It has a detrimental effect in the later stages of bacterial development and contributes to their destruction. Used intravenously, intramuscularly and orally;
Cephalexin. The drug does not allow the synthesis of components that make up the bacterial cell wall. It must be taken before meals, every 6 hours;
Cephalotin, which disrupts the ability of bacteria to divide normally, and also has a destructive effect on the membrane of staphylococci. Used both intravenously and intramuscularly;
Cefotaxime. The drug is aimed at suppressing the growth of bacteria, does not allow them to multiply. Apply both intravenously and intramuscularly. The dosage is selected individually;
Clarithromycin, which prevents bacteria from making their own proteins. It is most commonly used in tablet form, although it may be given intravenously for severe infections;
Erythromycin also interferes with protein production, must be applied every 6 hours;
Clindamycin is also aimed at eliminating the ability of bacteria to produce a certain protein, which leads to its death.
Before starting to use this or that remedy, it is necessary to conduct an antibiogram. This will help to identify the sensitivity of staphylococcus to a particular drug. Conducting such a study is relevant for the health of the patient, this will guarantee that the bacterium does not develop resistance.
Any antibacterial agents can be prescribed exclusively by the attending doctor and only after a thorough diagnosis.
Treatment of staphylococcal infection requires strict adherence to the frequency of administration, the time of use of the drug and its dosage. It is important to take the prescribed antibiotic not until the first symptoms disappear, and not less than 5 days. If it is necessary to extend the course, the doctor will inform about it. In addition, you can not stop treatment, therapy must be continuous.
Prevention in the fight against infection is a necessary measure, which doctors around the world repeat. Firstly, this is due to the fact that every year the bacterium becomes more and more resistant to antibacterial agents designed to eliminate it. This makes fighting infection especially difficult. Secondly, staphylococcus is capable of causing serious harm to the human body, so it is easier to prevent the development of inflammation than to fight it later. And thirdly, treatment with antibacterial agents always involves certain health risks in the form of various side effects.
Therefore, the following preventive measures will help maintain health:
Timely elimination of possible foci of infection. As sources, constantly inflamed tonsils, overgrown, not removed roots of teeth, boils, barley, inflammatory diseases of the genital area and urinary tract can serve. Any focus is a source of increased danger, which should be eliminated immediately. Moreover, harm can be done not only to their own health, but also to the health of those around them;
Prevention of SARS and seasonal influenza epidemics. In relation to the latter, it is advisable to undergo vaccination;
Cleanliness of the workplace, housing and clothing, ventilation of the premises, especially when a large number of people gather. It's no secret that not only clothing, but also dust is often contaminated with staphylococcus aureus. In addition, it is unacceptable to use other people's items for personal hygiene;
Going in for sports, rational nutrition, giving up bad habits, maintaining an active lifestyle. All this will strengthen the immune forces of the body and help it resist possible infection;
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene. In relation to the prevention of staph infection, it is most appropriate to talk about regular hand washing;
Eating clean, preferably thermally processed foods that have not expired. Often the source of infection is confectionery, canned food, poorly processed fruits and vegetables, as well as meat and milk from sick cows;
Timely treatment of wounds with antiseptic or antibacterial agents;
Visiting a doctor when the first symptoms of the disease are detected or if a possible infection is suspected;
Spherical bacteria are called "Staphylococcus aureus" or staphylococcus aureus. Many people ask what is it? These are pathogenic, gram-positive microorganisms that can take life without timely treatment. These microbes have a high survival rate.
They got their name from their appearance. The World Health Organization speaks of the development of these microorganisms in a fifth of all mankind. Staphylococcus aureus is formed as a natural background. The place of their distribution is the upper respiratory tract, the surface of the skin, the mucous membranes of the body.
American and Australian doctors reported cases from medical experience. These cases are united by diseases of Staphylococcus aureus.
These organisms can serve as the development of many diseases. Diseases are innocent and deadly. Therefore, they should be treated with special importance and seriousness. We describe the symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in adults and methods of treatment.
This type of bacteria was discovered by Alexander Ogston. This discovery was made in 1880. The first documentary evidence was found in 1884. In the 20th century of the 40s, experts began a deeper and more thorough study of these bacteria. Then experts noticed that these microbes are in good contact with the action of penicillin.
Official science distinguishes several types of cocci:
- Microorganisms methicillin - sensitive;
- Miticillin - resistant;
- Vancomycin - resistant;
- Glycopeptide - resistant;
Microorganisms methicillin
The first subspecies of bacteria was revealed as a result of mutations caused by the use of incorrect drugs and health cleansing of the body. This type of microorganisms is resistant to many medical drugs. Distinguished by its vitality. These types of staphylococcal microbes were the causative agents of such serious diseases as sepsis, pneumonia.
Diseases are difficult to cure with medications, and in most cases are fatal. You can become infected with such an infection in medical institutions where the attitude towards the patient is at a low level. People who have undergone various infections and have weak immunity are more susceptible. You can also catch this disease outside the hospital by contracting a skin infection.
Miticillin
The second type of golden disease is caused by domestic causes. The disease occurs due to mutations of classical bacteria. A staphylococcal infection looks like an ordinary insect bite. Therefore, in most cases, people do not show proper alertness.
A staph infection can be on the surface of the skin. The only distinguishing feature is the light liquid that appears when you press the so-called bite. Late or incorrect treatment of staphylococcus threatens with various complications, which is a great danger to the body. Antibiotics will not help in this case.
Vancomycin
The third type of infection is a mortal danger of the first type of staphylococcus aureus. They are very resistant to antibiotics, even vancomycin cannot help. This strain has the ability to copy the DNA of a neighboring microorganism and fully adapt to the body.
Glycopeptide
The fourth strain of infection is resistant to glycopeptide drugs, which are very effective antibiotics. Its positive qualities are comparable to vancomycin.
 Staphylococcus aureus can become infected at different ages. The toxins and enzymes found in these microorganisms can damage the body's cellular functions and damage tissues.
Staphylococcus aureus can become infected at different ages. The toxins and enzymes found in these microorganisms can damage the body's cellular functions and damage tissues.
There is a failure of the organs of destruction and severe intoxication. If you become infected with staph, the infection can spread throughout the body through the blood. The disease can be in two forms: intoxication and infectious.
The first form can manifest itself with weak immunity, in the form of poisoning of the body. Violates the functionality of internal organs, by getting infections into the blood. The second form of infections can destroy the surface of the skin on the body.
Staphylococcal infection does not appear immediately, but only after the following stages:
- Bacteria must pass the seeding stage on the surface of the skin of the body;
- Sticks can enter the body through a cut or abrasion;
- Further, the sticks will settle on the tissues inside the body;
- Then comes the fight against immunity;
- Only after all these stages, the tissue is destroyed.
When a staphylococcal infection becomes active, sepsis may be detected. To prevent this disease, you need to know the symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in adults.
Table of symptoms and their description
| Symptoms | Description |
| A sign of inflammation of the navel or omphalitis | A sign of inflammation of the navel or omphalitis. There are a number of factors for infection of the navel. Prerequisites for the disease, such as fistula, congenital pathologies, bladder duct, anatomical features, poor personal hygiene, navel piercings. |
| Redness around the navel | It is manifested by redness around the navel and fever. The navel in this case has a protruding shape. There is a wet stage of the disease, phlegmon and a stage of skin death, or a gangrenous form. The manifestation of such symptoms indicates an urgent observation by a surgeon. Usually this disease is treated with conservative methods, but with a fistula, surgical intervention cannot be avoided; |
| Purulent inflammation | Purulent inflammation on the skin can cause infection of the subcutaneous tissue. It can be boils, felons, abscesses, hydradenitis, pyoderma. They can be located on the glands that secrete sweat. Often accompanied by pain; |
| Lesions on the skin | Burn-like lesions on the skin. Convoyed by a clear liquid within these eruptions; |
| Inflammatory processes | Inflammatory processes on the skin. Manifested by redness, seals; |
| A symptom associated with conjunctivitis, that is, with an eye disease. | In this case, the mucous membrane of the eye acquires redness, roughness, clouding. In some cases, scars appear. The irritant of conjunctivitis can be dust, air, microbes, bright light, chemical and temperature reasons. At the first signs of this disease, you should contact an ophthalmologist. He will prescribe you timely treatment; |
| A symptom associated with rhinitis. | This is a disease of the nasal mucosa. Manifested by flows from the nose, headache, swelling of the shells, unpleasant feelings in the nose. If you have nasal congestion, you should consult an ENT specialist. It will help to identify the degree of the disease and prescribe a course of treatment; |
| A sign that is manifested by meningitis. | The disease makes itself felt at a high temperature. This is an inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord. It may appear suddenly or after a few days. People with head or spinal injuries are most susceptible to meningitis. Microbes associated with this disease are detected in serous, tuberculous, influenzal and herpetic forms. Treatment should be started as soon as symptoms are identified. It can stop or completely manage meningitis. Without timely treatment, death is possible. This symptom lasts from 2 to 6 weeks. With meningitis, you should contact a neurologist, ophthalmologist, phthisiatrician. |
| Inflammation of the urinary and genital tract | Purulent discharges are formed. This occurs with cystitis, urethritis, pyelonephritis. These diseases most often occur simultaneously. Pyelonephritis is an inflammation of the renal pelvis that occurs at any age. It affects the urethra and bladder. Urethritis is an inflammation of the urethra caused by viruses and bacteria transmitted through the genital tract. Also, this inflammation can be caused by injuries or allergic reactions of the body. Cystitis is an inflammation of the bladder, manifested by a violation of active functionality, a change in urine. The causes of occurrence are sexual infection, anatomical pathologies, allergic reactions, malignant tumors. Signs of these infections are burning, cramps, pain when passing urine; |
| Destruction of the skeletal system and joints | The destruction of the skeletal system and joints are caused by osteomyelitis and arthritis. Arthritis is characterized by fever, pain, swelling, and limitation of movement. Arthritis is also caused by gram-positive microbes. Treated with antibiotics and injections. Osteomyelitis is caused due to microorganisms that penetrate the bone due to traumatic injuries, operations. Also, the result of infection of the soft tissue and the blood system can be the cause of osteomyelitis. Manifestations of osteomyelitis can be acute, subacute or chronically sick in the skeletal system, febrile and leukocyte. On x-rays, bone destruction can be seen. Then abscesses and fistulas form. Osteomyelitis is diagnosed in the late period, so it is necessary to take x-rays as early as possible; |
| Various forms of intoxication | It can be vomiting and nausea manifestations; |
| Symptom associated with sepsis | Sepsis or blood poisoning is an infectious disease caused by the defeat of the pathogenic flora of the bloodstream. To date, sepsis is observed from 750 to 1.5 million people in the world. Statistics show that sepsis is manifested in a complicated form by abdominal, pulmonary and urogenital infections. In case of illness, it is necessary to seek help from a surgeon, a specialist in pulmonology, a urologist and a gynecologist. It is treated with modern antibiotic and chemical preparations. Lethal outcome is possible in 30 out of 50 percent of cases; |
Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in adults are manifested to a large extent and it is necessary to immediately contact specialists for timely treatment.
Signs of Staphylococcus aureus
When the above symptoms occur, the following diseases appear.
Furuncles
Furuncle disease, which is an acute purulent rash. The database of rashes is an ulcer with a light spot. Boils have a smooth appearance, when palpated, the nature of the seal is noticed, while the patient feels pain syndromes. Manifested in the neck, buttocks and face. With signs of a boil, it is necessary to remove the pus, so that after pressing, blood flows. Then you should wash the abscess, treating it with antiseptic ointments and drinking antibiotic preparations. If these measures are not followed, then serious consequences are possible.
Carbuncles
Carbuncles are a complicated type of boil, representing the combination of purulent rashes into one common abscess. When carbuncle manifests poor health, fever. Carbuncles should be disposed of with extreme caution and as quickly as possible. Delayed removal of the ulcer leads to the accumulation of bacteria in the focus of the rash.
watery sores
Bullous impetigo appears as watery ulcers, similar to a blister after a thermal burn. If the lesion is small, then it is necessary to apply antibiotics locally, and with a large area of \u200b\u200bthe skin lesion, doctors prescribe a course of antibiotic treatment inside.
Purulent subcutaneous formations
Phlegmon is an acute form of purulent subcutaneous formations. Without proper treatment, sepsis may occur.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia (a severe type of golden stick infection). It causes infection of the respiratory system, which occurs in the case of a weak organism. The disease affects different categories of age. Runs in severe form. It has a long recovery procedure, after which the body recovers for a long time. In this case, the patient may feel a high temperature and a feeling of chills.
Angina
Angina is manifested by the defeat of the tonsils. This is a highly contagious disease, the treatment period of which is two weeks. Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in adults are a kind of beacon for timely treatment.
Causes of infection with staphylococcus aureus bacteria:
- When hygiene rules are not observed;
- The rules of sanitation and safety of the premises are not observed;
- When in contact with sick people;
- Stay in a medical facility;
- Tattoos;
- Chronic diseases in severe forms.
 Staphylococcal infections are difficult to treat. People in such circumstances wonder how to treat this disease. The answer will be prompted by qualified specialists.
Staphylococcal infections are difficult to treat. People in such circumstances wonder how to treat this disease. The answer will be prompted by qualified specialists.
With an average degree, the treatment of staphylococcus aureus is penicillin and cephalosporins. The treatment period can vary from a week to a month. Treatment of staphylococcal infection with intoxication, possibly anatoxin-antistaphylococcal.
The patient is washed stomach with this drug. A course of vitamins of groups B and C, levamisole, taktivin is also prescribed. Preventive measures are important.
A prerequisite is the usual procedure for washing hands, after interacting with people, touching objects, contact with animals and any other parts of the environment. This preventive measure is simple and highly effective. It is also important to treat with antiseptic agents after contact with sick people.
Staphylococcus aureus is diagnosed by the following tests:
- Coagulase test in vitro;
- latex agglutination;
- General analyzes of urine and blood;
- biological seeding.
With the help of biological culture, doctors identify a strain of staphylococcus aureus bacteria. This is necessary to prescribe a specific course of antibiotics. To do this, doctors take a swab from the surface of the mouth and nasopharyngeal mucosa. This procedure must be carried out on an empty stomach. When taking crops from open wounds, a sterile swab is used. Analysis of urine and blood is known at the end of the day. These analyzes are also used for seeding.
Coagulase testing refers to qualitative reactions, consisting in the use of plasma from the patient's circulatory system. This plasma is used by the main material in which the marker substance is used. It stimulates the course of interaction, in case the stick enters the bloodstream. Latex testing is associated with a qualitative impact with a physical factor. In latex, they are retained on the outside by the expected microorganisms, which change their appearance with the help of antibodies.
Treatment of staphylococcal infection is carried out by non-traditional methods. Traditional medicine involves the use of decoctions and various tinctures. But such methods are not always able to help. Therefore, the treatment of staphylococcus should be carried out with medications.
Video: Symptoms and treatment of staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcal infection is a vital enemy that is difficult to deal with on your own. It is necessary to pay attention in time to the Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus in adults.
β-toxin or sphingomyelinase is detected in about a quarter of all pathogenic staphylococci. β-toxin can cause destruction of red blood cells ( red blood cells), as well as lead to the proliferation of fibroblasts ( migration of fibroblasts to the inflammatory focus). This toxin becomes most active at low temperatures.
γ-toxin is a two-component hemolysin, which has a moderate activity. It should be noted that the bloodstream contains substances that block the action of γ-toxin ( sulfur-containing molecules are able to inhibit one of the components of the γ-toxin).
δ-toxin is a low molecular weight compound with the property of a detergent. Exposure of the cell to δ-toxin leads to disruption of the integrity of the cell by various mechanisms ( mainly there is a violation of the relationship between the lipids of the cell membrane).
- exfoliative toxins. In total, 2 types of exfoliative toxins are distinguished - exfoliant A and exfoliant B. Exfoliative toxins are detected in 2-5% of cases. Exfoliants are able to destroy intercellular bonds in one of the layers of the skin ( granular layer of the epidermis), and also lead to detachment of the stratum corneum ( the most superficial layer of the skin). These toxins can act locally and systemically. In the latter case, this can lead to scalded skin syndrome ( the appearance of areas of redness on the body, as well as large blisters). It should be noted that exfoliants are able to bind several molecules involved in the immune response at once ( exfoliative toxins exhibit properties of superantigens).
- Toxic shock syndrome toxin (formerly called enterotoxin F) is a toxin that causes the development of toxic shock syndrome. Toxic shock syndrome is understood as an acute polysystemic organ damage ( multiple organs are affected) with fever, nausea, vomiting, impaired stool ( diarrhea), skin rash. It is worth noting that the toxic shock syndrome toxin is capable of producing in rare cases only Staphylococcus aureus.
- Leukocidin or Panton-Valentine toxin capable of attacking some white blood cells ( neutrophils and macrophages). The effect of leukocidin on the cell leads to a violation of the water and electrolyte balance, which increases the concentration of cyclic adenosine monophosphate in the cell ( cAMP). These disorders underlie the mechanism of occurrence of staphylococcal diarrhea in food poisoning with products infected with Staphylococcus aureus.
- Enterotoxins. In total, there are 6 classes of enterotoxins - A, B, C1, C2, D and E. Enterotoxins are toxins that affect human intestinal cells. Enterotoxins are low molecular weight proteins ( proteins), which tolerate high temperatures well. It should be noted that it is enterotoxins that lead to the development of food poisoning by the type of intoxication. In most cases, these poisonings are capable of causing enterotoxins A and D. The effects of any of the enterotoxins on the body are manifested in the form of nausea, vomiting, pain in the upper abdomen, diarrhea, fever and muscle spasm. These disorders are due to the superantigenic properties of enterotoxins. In this case, there is an excessive synthesis of interleukin-2, which leads to this intoxication of the body. Enterotoxins can lead to an increase in the tone of the smooth muscles of the intestine and increase motility ( bowel contractions to move food) gastrointestinal tract.
Enzymes
Staphylococcal enzymes have a variety of actions. Also, the enzymes that staphylococci produce are called "aggression and defense" factors. It should be noted that not all enzymes are pathogenicity factors.The following staphylococcal enzymes are distinguished:
- catalase is an enzyme that can break down hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is able to release the oxygen radical and oxidize the cell wall of the microorganism, leading to its destruction ( lysis).
- β-lactamase able to effectively fight and neutralize β-lactam antibiotics ( a group of antibiotics that are united by the presence of a β-lactam ring). It should be noted that β-lactamase is very common among the population of pathogenic staphylococci. Some strains of staphylococci show increased resistance to methicillin ( antibiotic) and other chemotherapy drugs.
- Lipase is an enzyme that facilitates the attachment and penetration of bacteria in the human body. Lipase is able to break down fat fractions and in some cases penetrate through the sebum into the hair follicle ( location of the hair root) and sebaceous glands.
- Hyaluronidase has the ability to increase the permeability of tissues, which contributes to the further spread of staphylococci in the body. The action of hyaluronidase is aimed at the breakdown of complex carbohydrates ( mucopolysaccharides), which are part of the intercellular substance of the connective tissue, and are also found in the bones, in the vitreous body and in the cornea of the eye.
- DNAase is an enzyme that cleaves the double-stranded DNA molecule ( Deoxyribonucleic acid) into fragments. During exposure to DNase, the cell loses its genetic material and the ability to synthesize enzymes for its own needs.
- fibrinolysin or plasmin. Fibrinolysin is a Staphylococcus enzyme that is able to dissolve fibrin strands. In some cases, blood clots perform a protective function and do not allow bacteria to penetrate other tissues.
- Staphylokinase is an enzyme that converts plasminogen to plasmin when exposed to staphylokinase, the proenzyme plasminogen is converted to its active form - plasmin). Plasmin is extremely effective in breaking down large blood clots that act as an obstacle to the further advancement of staphylococci.
- Phosphatase is an enzyme that accelerates the process of splitting esters of phosphoric acid. Staphylococcus acid phosphatase is generally responsible for the virulence of the bacterium. This enzyme can be located on the outer membrane, and the location of the phosphatase depends on the acidity of the medium.
- Proteinase Staphylococcus is able to break down proteins into amino acids ( protein denaturation). Proteinase has the ability to inactivate certain antibodies, suppressing the body's immune response.
- Lecithinase is an extracellular enzyme that breaks down lecithin ( fat-like substance that makes up the cell wall) into simpler components ( phosphocholine and diglycerides).
- Coagulase or plasmacoagulase. Coagulase is the main factor in the pathogenicity of staphylococcus. Coagulase is capable of inducing blood plasma clotting. This enzyme can form a thrombin-like substance that interacts with prothrombin and envelops the bacterium in a fibrin film. The formed fibrin film has significant resistance and serves as an additional capsule for staphylococcus aureus.
Groups of staphylococci depending on the presence of coagulase
| pathogenicity | Coagulase-positive staphylococci | Coagulase-negative staphylococci |
| Opportunistic staphylococci living on the skin and mucous membranes of humans and animals | S. intermedius, S. hyicus | S. capitis, S. warneri, S. cohnii, S. xylosis, S. sciuri, S. simulans, S. arlettae, S. auricularis, S. carnosus, S. caseolyticus, S. gallinarum, S. kloosii, S. caprae, S. equorum, S. lentus, S. saccharolyticus, S. schleiferi, S. lugd unensis, S. chromogenes. |
| Pathogenic staphylococci that cause disease in humans | S. aureus ( Staphylococcus aureus) | S. saprophyticus ( saprophyticstaphylococcus aureus), S. epidermidis ( epidermalstaphylococcus aureus), S. haemolyticus ( hemolytic staphylococcus aureus). |
Adhesins
Adhesins are proteins of the surface layer, which are responsible for the attachment of staphylococcus to the mucous membranes, to the connective tissue ( ligaments, tendons, joints, cartilages are some of the representatives of the connective tissue), as well as to the intercellular substance. The ability to attach to tissues is related to hydrophobicity ( property of cells to avoid contact with water), and the higher it is, the better these properties are manifested.Adhesins have specificity for certain substances ( tropism) in organism. So, on the mucous membranes, this substance is mucin ( a substance that is part of the secretion of all mucous glands), and in the connective tissue - proteoglycan ( intercellular substance of connective tissue). Adhesins are able to bind fibronectin ( complex extracellular substance), thereby improving the process of attachment to tissues.
It should be noted that most of the components of the cell wall of pathogenic staphylococci, as well as their toxins, can lead to allergic reactions of a delayed and immediate type ( anaphylactic shock, Arthus phenomenon, etc.). Clinically, this manifests itself in the form of dermatitis ( inflammatory disease of the skin), bronchospastic syndrome ( spasm of the smooth muscles of the bronchi, which manifests itself in the form of shortness of breath) etc.
Method of infection with staphylococcus aureus
 Diseases caused by staphylococci can be self-infected ( entry of bacteria into the body through damaged areas of the skin and mucous membranes), since staphylococci are permanent inhabitants of the skin and mucous membranes of humans. Infection can also occur through contact with household items or by eating contaminated food. This method of infection is called exogenous.
Diseases caused by staphylococci can be self-infected ( entry of bacteria into the body through damaged areas of the skin and mucous membranes), since staphylococci are permanent inhabitants of the skin and mucous membranes of humans. Infection can also occur through contact with household items or by eating contaminated food. This method of infection is called exogenous. It should be noted that the carriage of pathogenic staphylococci is of great importance in the mechanism of transmission of staphylococci. The concept of "carriage" means the presence of pathogenic bacteria in the body that do not cause any clinical manifestations of the disease. There are two types of carriage of pathogenic staphylococci - temporary and permanent. The main danger is posed by people who are constant carriers of pathogenic staphylococcus aureus. In this category of persons, pathogenic staphylococci are detected in large numbers, which are contained for a long time on the mucous membranes and in the skin. It is still not entirely clear why there is a long-term carriage of pathogenic staphylococcus aureus. Some scientists attribute this to a weakening of local immunity with a decrease in the titer of immunoglobulin A ( a decrease in the concentration of one of the types of antibodies that are responsible for the immune response). There is also a hypothesis that explains the long-term carriage of pathogenic staphylococcus aureus with impaired functioning of the mucous membrane.
The following mechanisms of transmission of staphylococci are distinguished:
- contact-household mechanism;
- airborne mechanism;
- air-dust mechanism;
- alimentary mechanism;
- artificial mechanism.
Contact household mechanism
The contact-household mechanism of infection transmission occurs due to the entry of bacteria from the skin and mucous membranes to various household items. This route of transmission is associated with the use of common household items ( towel, toys, etc.). To implement the contact-household transmission route, a susceptible organism is required ( when introducing bacteria, the human body reacts with a clinically pronounced disease or carriage). The contact-household transmission mechanism is a special case of the contact route of infection transmission ( direct skin contact).Air drop mechanism
The airborne transmission mechanism is based on the inhalation of air, which contains microorganisms. This transmission mechanism becomes possible if bacteria are released into the environment along with exhaled air ( with diseases of the respiratory system). Isolation of pathogenic bacteria can be carried out through breathing, coughing and sneezing.Air dust mechanism
The airborne mechanism of transmission of staphylococcal infection is a special case of the airborne mechanism. The air-dust mechanism is realized with long-term preservation of bacteria in dust.Alimentary mechanism
With the alimentary mechanism ( fecal-oral mechanism) transmission The excretion of staphylococci occurs from the infected organism with a bowel movement or with vomiting. The penetration of bacteria into a susceptible organism is carried out through the oral cavity when contaminated food is consumed ( the presence of microorganisms in food). After that, staphylococcus again colonizes the digestive tract of the new host. As a rule, the contamination of food with staphylococci occurs due to non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene - insufficient hand treatment. Also, this mechanism can be implemented due to the carriage of a staphylococcal infection in a food industry worker.Artifical mechanism
The artificial transmission mechanism is characterized by the penetration of pathogenic staphylococcus into the human body through insufficiently sterilized ( sterilization - a method of processing medical instruments and equipment to completely destroy all microorganisms) medical instruments. As a rule, this can occur during the use of various instrumental diagnostic methods ( e.g. bronchoscopy). Also, in some cases, the penetration of staphylococcus into the body is observed during surgical operations.It should be noted that medical equipment and instruments may not be completely sterile due to the fact that staphylococcus is resistant to certain types of disinfectants ( chemicals with antimicrobial activity). Also, the reason for the artifactual mechanism of transmission may be the incompetence or negligence of medical personnel.
What diseases are caused by Staphylococcus aureus?
 Staphylococcus aureus is capable of infecting most tissues of the human body. In total, there are more than a hundred diseases caused by a staphylococcal infection. Staphylococcal infection is characterized by the presence of many different mechanisms, routes and factors of transmission.
Staphylococcus aureus is capable of infecting most tissues of the human body. In total, there are more than a hundred diseases caused by a staphylococcal infection. Staphylococcal infection is characterized by the presence of many different mechanisms, routes and factors of transmission. Staphylococcus aureus can very easily penetrate through minor damage to the skin and mucous membranes into the body. Staphylococcal infection can lead to a variety of conditions ranging from acne ( acne) and ending with peritonitis ( inflammation of the peritoneum), endocarditis ( inflammation of the inner lining of the heart) and sepsis, which is characterized by mortality in the region of 80%. In most cases, staphylococcal infection develops against the background of a decrease in local or general immunity, for example, after an acute respiratory viral infection ( SARS).
Staphylococcal sepsis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- increase in body temperature up to 39 - 40 ° C;
- intense headache;
- loss of appetite;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- increased sweating;
- skin pustular rash;
- increase in the number of heartbeats up to 140 beats per minute;
- an increase in the size of the liver and spleen;
- loss of consciousness;
- rave.
Staphylococcus aureus is a spherical bacterium belonging to the genus Staphylococcus aureus. For the first time this microorganism was discovered in 1880 by the Scottish surgeon Alexander Ogston in the composition of pus pumped out from surgical abscesses. Staphylococcus got its name due to its appearance: unlike many colorless bacteria, representatives of this species have a golden hue due to the presence of pigments of the carotenoid group.
According to statistics, the presence of this microorganism is detected on the skin and on the mucous epithelium of the upper respiratory tract in 20% of the population. Staphylococcus aureus is considered the main causative agent of a number of diseases, ranging from skin infections (boils, carbuncles, phlegmon) to such deadly pathologies as endocarditis, osteomyelitis and sepsis.
Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus
In the process of life, staphylococcus produces various enzymes and toxins that have a detrimental effect on the human body. For example, staphylococcal toxin exfoliatin can damage skin cells, enterotoxin can cause symptoms of food poisoning, and leukocidin can destroy white blood cells. For this reason, the symptoms of diseases provoked by Staphylococcus aureus vary significantly and depend on the localization of the focus of infection, the presence or absence of concomitant diseases in a sick person, on the state of his immunity and on the degree of exposure to environmental factors.
Infection with Staphylococcus aureus of the skin is accompanied by the appearance of impetigo, acne, acne, phlegmon, boils, carbuncles or abscesses on the surface of the skin. Getting on the mucous epithelium of the throat or, a staphylococcal infection provokes the occurrence of otitis media, sinusitis and other inflammatory pathologies of the upper respiratory tract or upper respiratory tract.
With the defeat of Staphylococcus aureus, the lungs develop, characterized by the appearance of shortness of breath and chest pain, severe intoxication of the body and the formation of many purulent formations in the lung tissues, gradually transforming into abscesses. With the breakthrough of abscesses into the pleural cavity, suppuration of the pleura (empyema) develops. The entry of Staphylococcus aureus into the region of the brain is one of the causes of the development of meningitis or thrombophlebitis of the cerebral veins.