Today, the diagnosis of “cervical erosion” occurs quite often, in almost every third woman. Erosion refers to defects in the superficial layer of cells covering the cervix. There are two forms of it: true and false (pseudo-erosion).
Erosion: forms, signs and causes
The first form is an ulcer that occurs on the walls of the cervix due to damaged epithelial cells as a result of mechanical action, for example, surgical abortion, traumatic insertion of a tampon, or rough sexual intercourse. In the absence of infections and hormonal disorders, such erosion can heal on its own. But the second form, false erosion, is much more dangerous.
It is a response to the formation of cervical defects. In their place, the mucous membrane begins to grow and a large inflamed area forms. Such erosion should be treated to prevent it from growing. After all, places of damage are a very favorable environment for various types of infections.
The insidiousness of this disease is that it practically does not manifest itself, especially in the early stages. Sometimes there may be spotting after intercourse or simply for no reason in the middle of the cycle. As a rule, women do not pay attention to this, and only learn about the existence of erosion at a scheduled appointment with a gynecologist. However, the absence of symptoms does not mean that you should ignore this fact and postpone treatment. Many nulliparous women do this because there is an opinion that cauterization can lead to complications during childbirth. Let's figure out how true this is.

Cauterize or wait
It is believed that it is prohibited for nulliparous representatives of the fair sex to cauterize erosion. The reason for this prohibition is that after the cauterization procedure, a scar remains, which prevents the cervix from opening during childbirth, as a result of which it begins to stretch poorly and tear. Therefore, all methods of treating erosion in nulliparous women should be excluded, the consequences of which may be:
- scar formation;
- severe damage to soft tissues;
- spontaneous dilation of the cervix, which during pregnancy threatens miscarriage.
Until recently, the most common method of treating erosion was cauterization with electricity, which led to all of the above consequences. That is why it does not apply to nulliparous women. But this does not mean that they do not need to treat erosion at all, since delaying therapy can lead to dangerous complications. We are talking about malignant degeneration of cells in the damaged area.
Cauterization in the traditional sense is, of course, undesirable for the cervix of a nulliparous woman. However, today there are various ways to combat erosion that are suitable for everyone, including those who have not yet become a mother.

Gentle treatment methods
Treatment of cervical erosion in nulliparous women and girls is carried out only with gentle methods, after which scars and adhesions do not form. Today there are several such methods. Which one to use is decided only by the doctor individually for each patient.
- Drug treatment. This method is appropriate for untreated erosion accompanied by inflammatory processes. This treatment is carried out immediately for both sexual partners. In this case, during treatment you should avoid sexual intercourse or be sure to use a condom.
- Cryodestruction or freezing. Treatment involves applying liquid nitrogen to the affected area. As a result, damaged cells freeze and die. In this case, healthy cells are not affected. The procedure is painless and does not cause bleeding after it is performed. There are no scars left on the cervix and it is not deformed.
- Laser therapy. The essence of the method is the direct impact of a laser beam on the affected tissue. The laser beam penetrates to the required depth and destroys the affected cells without affecting adjacent healthy tissue. The vessels are immediately welded, so rapid healing occurs, and no traces remain at the wound site. The method is highly effective and safe.
- Cauterization by radio waves. It is carried out using the Surgitron apparatus. The procedure is painless, but you may experience some bleeding for several days afterwards. You should abstain from sex for 2-3 weeks. And after 4-5 weeks, visit a gynecologist for a follow-up examination.
- Cauterization with drugs. Impact on the affected areas and destruction of diseased cells is possible with the help of drugs such as Solkovagin and Vagotil. The first drug allows you to cope with erosion in one procedure. In the second case, several procedures may be required.
Each method is aimed at destroying the affected cells, however, unlike electrocoagulation, the above methods do not entail undesirable consequences for women who are yet to become pregnant and give birth. Often, minor erosion at the initial stage is only observed by a gynecologist before treatment is prescribed.
It should be remembered that there are no universal methods for treating erosion, especially in nulliparous women. Only a doctor can assess her character and prescribe the most appropriate treatment with minimal consequences for the patient.
In any case, you cannot ignore the condition of the cervix without attention and let the disease take its course. Over time, it progresses and can lead to unwanted dangerous consequences. Therefore, you should regularly visit your gynecologist for a routine examination, even if nothing bothers you.
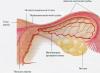
Erosion (ectopia, endocervicosis, pseudo-erosion) of the cervix is found in half of the girls and women of reproductive age. Visually, the disease is defined as redness in the area of the external opening of the cervix (the spot may not always cover the entire surface of the opening).
Erosion occurs when the cells lining the inside of the canal migrate to the vaginal area. Cervical erosion occurs in nulliparous women, children, girls and women who have given birth. This is due to the process of formation of the girl’s reproductive system in utero: the entire surface of the vagina and canal is first lined with columnar epithelial cells (internal cells), and later they are gradually displaced and replaced by flat epithelium (external cells).
Causes of the disease
The location of the epithelium in the vagina is influenced by many factors. The causes of cervical erosion in nulliparous women are:
- The infectious nature of genital diseases (including STIs (sexually transmitted infections) caused by ureaplasma, gonorrhea, chlamydia or trichomonas).
- Viral lesions of the internal genital organs (human papilloma, herpes).
- Physical influences (sexual intercourse, surgical interventions, abortion).
- Endocrine disorders in a woman’s body (including taking hormonal contraceptives).
- Inflammatory diseases.
- Metabolic diseases (diabetes mellitus).
- Installation of an intrauterine device.
- Irregular menstruation.
- Frequent change of sexual partner.
Symptoms of cervical endocervicosis
In most patients, ectopia does not manifest itself, but there are some signs that suggest the presence of the disease:
- Pain during sexual intercourse or immediately after intimate intercourse (pain can be mild or intense, pulling, cramping).
- The appearance of brown vaginal discharge or streaks of blood after sex.
- Leucorrhoea that accompanies a woman throughout her menstrual cycle.
- Frequent relapses of candidiasis (more than once in a 3-week period).
Even if there are no symptoms, there is no guarantee that there is no disease either. For timely detection and treatment of cervical erosion in women who have not given birth to children, it is necessary to undergo examination by a gynecologist twice a year.

Diagnosis of the disease
When visiting a doctor, it is necessary to conduct a number of studies to confirm or refute the diagnosis:
- Gynecological examination on a chair using mirrors.
- Special examination using the optical instrument of a colposcope (colposcopy).
- A smear is taken to examine the vaginal flora.
- A cytological examination of the smear is performed.
If the gynecologist suspects ectopia, then before starting therapy it is necessary to check the eroded area for the presence of malignant neoplasms. To do this, a biopsy is performed (separation of a small area of atypical epithelium) followed by identification of the tissue material.
During the research, the woman does not experience pain. During the biopsy, discomfort and slight bleeding may occur in the following hours.
Why does erosion need to be treated?
There is a possibility of independent transition of the epithelium of the inner lining surface of the opening of the cervix into squamous epithelium located on the walls of the vagina. This process may be accompanied by the formation of a scar, which leads to a decrease in the elasticity of the cervix. This increases the likelihood of complications during pregnancy and childbirth:
- Risk of fetal asphyxia during passage of the cervix due to its inelasticity.
- During natural childbirth, an inelastic area of tissue can be injured (torn), the wound surface is highly susceptible to various diseases (candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, various STIs, viruses, including the human papillomavirus).
- If rigid (inelastic) tissues rupture during pregnancy, then there is a possibility of miscarriage and intrauterine death due to infection.
Another risk is associated with the ability of the eroded area to malignize (transition into a malignant tumor). According to statistics, the number of detections of cancerous tumors on the cervix increases every year. Doctors associate this process, among other things, with untimely treatment of ectopia.
Why should nulliparous women not be able to use certain therapies?
If the treatment method is incorrectly selected, scarring may form and the canal may become fused. The consequence of the latter is infertility. If serious injuries occur, insufficiency may develop, causing spontaneous dilatation of the cervix during pregnancy (risk of miscarriage).
Therefore, it is necessary to carefully select a technique. Treatment of cervical erosion in nulliparous women cannot be carried out using cauterization methods, exposure to low temperatures (cryodestruction), or electrical destruction. All of the above methods have a high probability of scar formation, canal adhesions, menstruation disorders, exacerbations of inflammatory diseases, extensive wound surface and destruction of healthy squamous epithelium. In addition, rehabilitation sometimes takes from one to three months; it is necessary to abstain from sexual relations, bathing, and physical activity. During the procedures themselves, the patient experiences pain.
Treatment methods for nulliparous women
There are several methods to cure the disease in all categories of women. First of all, this is the impact of chemical agents. Modern drugs containing mixtures of acids that selectively act on columnar epithelial cells do not damage normal cells. Such chemicals include:
- Vulnostimulin.
- Vagotil.
- Solkovagin.
The wound surface heals quickly and no scar is formed.
Treatment of cervical erosion in nulliparous women can be carried out with laser beams (CO2 laser and helium-neon laser are used). In combination, these 2 lasers allow you to achieve 100% results. When using laser treatment for ectopia, wound healing occurs faster than with cryodestruction or electrocoagulation.
Another most gentle method of erosion therapy is a non-contact radio wave surgery device.
Since changes in the cells lining the cervix can be caused by an STI, it is necessary to first undergo tests to identify them and, if necessary, treat them. It is also necessary to cure inflammatory diseases and thrush. In some cases, this is enough to completely cure cervical endocervicosis. If this does not happen, the doctor will prescribe suitable treatment.
There are alternative methods of treating ectopia that can be used in nulliparous women, these include:
- Hirudotherapy (use of leeches).
- Using tampons with herbal ingredients from various manufacturers.
- Using self-prepared solutions based on herbal ingredients for use as tampons.
Such techniques are not widely used and their effectiveness has not been scientifically proven. If you wish to use them, a mandatory consultation with a gynecologist is necessary.
The cervix connects the internal genital organs to the vaginal canal. Damage to the epithelium of the vaginal area can cause infertility, and degeneration of epithelial cells leads to the development of a malignant tumor of the uterus. Often a woman does not even know about the existence of the pathology. Symptoms of concomitant diseases that cause damage to the epithelium may be concerning. During an examination for ailments or during a preventive examination, the gynecologist detects erosion. It is necessary to choose a suitable treatment method.
Content:
What is cervical erosion
The inner surface of the cervix is covered with mucous membrane. Moreover, the composition of the epithelium in the area of the cervical canal itself and its outer part extending into the vagina is different. The cells of the internal epithelium are cylindrical in shape, and in the outer part they are flat. Erosion occurs when cracks appear on the vaginal part of the canal, into which columnar epithelium from the neighboring area enters. As it grows, it narrows and even blocks the opening of the cervix, which leads to infertility. Cancerous degeneration of cells is also possible.
Erosion is often confused with cervical ectopia. Ectopia is a harmless movement of a small part of the columnar epithelium into the area of flat epithelium. In this case, at the junction of the two layers around the exit from the channel, a bright pink stripe is formed, which is easily confused with erosion. Ectopia is called pseudo-erosion.
Is it necessary to treat erosion in nulliparous women?
Ectopia often appears in nulliparous young women. It appears as a result of hormonal disorders and inflammatory processes. After eliminating inflammation and establishing hormonal levels, this disorder can go away on its own, and the normal state of the epithelium is restored.
Treatment of women, especially nulliparous women, for cervical erosion is not required if they are not bothered by any painful symptoms. It is only recommended to undergo regular gynecological examinations to prevent complications. Treatment is mandatory in the following cases:
- Simultaneously with ectopia, the woman has a chronic inflammatory disease that is difficult to treat.
- A woman is diagnosed with papillomavirus or another infection, and there are complaints of unusual bloody discharge from the genital tract, pain in the lower abdomen, and in the lower back.
- If copious mucous discharge appears, there are cysts.
- In the presence of cervical dysplasia. Dysplasia occurs due to the fact that the inside of the cervical canal turns outward. This condition often occurs in newborns, but by the time of puberty it goes away on its own. If dysplasia does not disappear, then the cylindrical epithelium remains outside and can degenerate into cancer. In this case, the pathology requires mandatory treatment, regardless of whether the woman intends to give birth in the future or not.
Warning: A malignant tumor in the vaginal area of the uterus in the initial stage is difficult to distinguish by appearance from erosion, therefore, to establish an accurate diagnosis, a routine gynecological examination is not enough; colposcopy is required.
Video: Causes of cervical erosion, need for treatment
Diagnosis of erosion
Erosion is detected during a gynecological examination using speculum. The area of erosion is distinguished by a brighter color and granular structure of the epithelium. To study the changes in detail and establish their benign or malignant nature, the colposcopy method is used. A colposcope helps to examine the affected area with optical magnification and lighting. This allows you to distinguish true erosion from ectopia and detect changes characteristic of a cancerous tumor. At the same time, a biopsy of the suspicious area can be done (for this, a piece of tissue is cut out). A smear is also taken to detect infection and study microflora.
A cytological examination of the affected area is performed. To do this, using a spatula and brush, a scraping is taken from the surface of the cervix (the procedure is painless). The material is then examined under a microscope. The composition and nature of the tissues of the affected area are examined. A smear of the cervix is taken to detect papillomavirus (a common cause of cancer).
The danger of treating erosion in women without children
When treating erosion, the affected cells are destroyed. This can also damage healthy tissue. When they are mechanically removed using various cauterization methods, scars remain on the neck, and fusion of the canal walls can occur. This leads to infertility.
Scarring causes the tissue to lose its elasticity. During childbirth, this may cause ruptures in the cervix. Scarring leads to the fact that the cervix will spontaneously open during pregnancy, causing a miscarriage. Due to fear of complications during pregnancy and childbirth, nulliparous women sometimes delay treatment for cervical erosion until the birth of the child. However, the doctor must decide what to do after the examination.
Erosion is treated in two ways: cauterization and chemofixation. For cauterization the following are used:
- liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction);
- electricity;
- radio waves;
- laser radiation.
Video: What is ectopia. How to treat erosion in nulliparous women
What methods are used to treat erosion in nulliparous women?
Cervical erosion in nulliparous women is most often treated with chemofixation. Preparations (Vulnostimulin, Vagotil, Solkovagin) containing a mixture of acids are used. When treating the affected surface, they destroy diseased cells without damaging healthy ones. After treatment, the wound heals quickly without leaving scars.
Non-contact laser cauterization and radio wave methods are also used to treat nulliparous women. Their advantage is that healing occurs much faster than using contact methods. No scars are formed.
To regenerate the mucous membrane during erosion in nulliparous women, suppositories (Depantol, Hexicon) are also used for insertion into the vagina. Other methods are used for nulliparous women only if absolutely necessary.
Article last updated 12/07/2019
Therapy of erosive lesions is carried out mainly by cauterization. Drug therapy is rarely used due to its low effectiveness. Cervical erosion in nulliparous women is often diagnosed. In such a case, treatment requires a particularly careful approach so as not to damage the soft structures of the organ and not provoke a number of consequences, the most dangerous of which is infertility.
The optimal method is selected individually, taking into account the factors causing cervical erosion. The causes of erosion should be treated simultaneously with the removal of pathological foci in order to reduce the risk of relapse in the future.
Is it necessary to treat cervical erosion in nulliparous women? When the lesions are small in size, and the disease is congenital in nature, there is no growth dynamics, treatment may not be carried out.
It is mandatory to cauterize cervical erosion in nulliparous women in the following cases:
- inflammation occurring in the chronic stage;
- infections that are transmitted through sexual contact (unprotected);
- cystic formations in the ovaries;
- uterine dysplasia.
With these concomitant diseases, it is important to understand why the pathology is dangerous. In this case, the risks of developing complications increase, for example, with papillomavirus, there is a possibility of benign cells degenerating into an oncological tumor. In the presence of such pathologies and conditions, it is necessary to treat erosion urgently. Therapy is also carried out in cases where the symptoms of the disease are severe.
Causes and symptoms
Methods for treating cervical erosion in nulliparous women are selected individually in each case. But before prescribing the most effective method, it is necessary to find out where this disease came from. Causes of cervical erosion in nulliparous women:
- hormonal disbalance;
- previous surgical interventions in the area of reproductive organs;
- presence of infectious diseases.
Other causes of cervical erosion in nulliparous women:
- genital herpes;
- presence of diabetes mellitus;
- promiscuous sex life;
- mechanical damage to the organs of the reproductive system (the most common cause);
- installed intrauterine device;
- long-term use of hormonal oral contraceptives;
- presence of sexually transmitted diseases.
Symptoms may not have a specific severity for a long time. Possible signs include: pain during sex, disruptions in the menstrual cycle, discharge in the middle of the cycle, candidiasis.
For nulliparous women, treatment of cervical erosion is not recommended using cauterization. All common methods of removing pathological lesions can provoke the formation of scars, cicatricial formations, narrowing of the cervical canal, hormonal imbalance and menstruation disorders.
In nulliparous girls, cervical erosion is treated with cauterization only when most of the organ is damaged by pathological foci, and other methods recommended for nulliparous girls are ineffective.
Diathermocoagulation is a cauterization method that cannot be used for nulliparous women. The essence of the procedure is to apply electric current to erosive lesions.
Why is it strictly prohibited to treat erosion in nulliparous women using this technique? This ban is due to the fact that there is a high probability of scar formation on the soft tissue of the organ.
The consequences of diathermocoagulation can be the following - infertility, bleeding, development of inflammation. A large affected area cannot be treated this way the first time. The procedure will need to be repeated, which in turn further increases the risk of complications.
Application of chemical acids
In nulliparous girls, erosion is treated mainly by applying chemicals to the lesions. These medications are made using acid mixtures that have a selective effect (they affect only areas of the altered epithelium), while healthy tissue is not damaged. It is recommended to treat cervical erosion in a woman who has not yet given birth with the following chemicals:
- Vagotil;
- Solkovagin;
- Vulnostimulin;
- Cycloferon.
The disadvantages of such drugs are that the therapy does not eliminate the very causes of cervical erosion, so they must be treated separately. In addition, up to 5 procedures may be required to completely remove erosive lesions.
Cauterization of erosion with Solkovagin is carried out if a woman is diagnosed with ectopia.
Pathology therapy with Cycloferon is carried out in cases where cervical erosion in a nulliparous girl is caused by the presence of viral diseases.
Alternative techniques
Conservative methods of treating cervical erosion are not highly effective and are mostly used when a woman has contraindications to the use of other, more reliable methods. A gynecologist can tell you in more detail how to treat erosion without surgical and chemical intervention, and what methods to use. As a rule, this is used:

- hirudotherapy;
- insertion of tampons with medications;
- solutions based on decoctions of medicinal herbs.
These methods, although used in gynecology to remove cervical erosion in nulliparous women, are considered controversial by most doctors. Many experts consider them completely ineffective.
Radio waves

Radio wave cauterization can be used to treat cervical erosion in nulliparous women. The method is painless, the procedure is quick. Side effects: Minor bleeding may occur. Healing and recovery occur within a month. There is no chance of scar formation.
Destruction by liquid nitrogen
Is it possible to cauterize erosion in nulliparous women using cryodestruction? The method of treating pathological lesions with liquid nitrogen is considered safe and approved by doctors.
The advantage of the technique is that there is virtually no risk of severe complications. Removal with liquid nitrogen is used in cases where the pathological foci are small and adjacent soft structures are not affected.
Cauterization with laser
How is cervical erosion treated in nulliparous women to prevent the development of complications? For these purposes, a laser technique is used, which is characterized by a sufficient degree of safety and efficiency. Since the risks of complications in the future are minimal, the laser can be used in nulliparous girls.
The laser beam is directed clearly at the affected organ structures, as a result of which there is no likelihood of damage to healthy tissue. Despite the fact that there is no risk of scar formation after laser cauterization, doctors are reluctant to use this method on women who have not given birth.
Possibility of pregnancy after treatment

To the question of whether this pathological process needs to be treated, the answer is unequivocal - it is necessary, otherwise serious complications may arise. In the early stages, it is not difficult to cure the disease in girls who have not yet given birth. The main thing is to address this issue in a timely manner. The chances of conceiving and giving birth after proper treatment are high.
Prevention
It is not known for certain where the pathological change in the epithelial cells of the organ comes from. The presence of provoking factors increases the likelihood of the formation of pathological foci on the cervix, but is not a mandatory requirement for this.
To prevent such an unpleasant disease from appearing, a woman needs to be attentive to her female health, regularly visit a doctor for a preventive examination and promptly treat concomitant diseases (inflammatory and infectious), and do not forget about the need to protect yourself when having sex with an untested partner.
What is cervical erosion in a nulliparous girl, and how does this pathology threaten the health and life of the patient? Modern doctors do not give a definitive answer to this question. To understand the problem in more detail, we will consider the nature of the development of the pathology, symptoms, treatment and possible consequences.
Nature of development and symptoms of pathology
Cervical erosion is a spectrum of pathologies, based on the formation of various defects in the epithelial tissue of the uterine cavity, with the further development of inflammatory processes provoked by the activation of aggressive foreign flora.
Cervical erosion in most cases is accompanied by characteristic symptoms. Namely, this:
- the presence of pain localized in the lower abdomen;
- disturbances of the monthly cycle;
- characteristic bloody or mucous vaginal discharge of non-ovulatory origin;
- feeling of general weakness, dizziness;
- pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse;
- difficulties conceiving a child.
The reasons for the development of pathology can be very different - from hormonal imbalances to a previous infectious disease of the genital tract.
Among the pathogenic microorganisms that most often cause cervical erosion are chlamydia, trichomonas, mycoplasma and ureaplasma, and human papillomavirus.
All these pathogens are capable of aggressively affecting the affected epithelial tissue and promoting the development of an abscess, as a result of which the formation of malignant tumors and the development of oncological pathologies is possible in the reproductive organs of the female body. The influence of inflammatory processes in the uterus on a woman’s body as a whole can be characterized by extremely negative consequences.
Features of treatment
In the past, cauterization of erosion was considered a universal method of treating pathology. However, modern medical research has proven not only the questionable effectiveness of the method, but also its detrimental effect on the woman’s body.
After using the cauterization method, specific scars are formed on the walls of the uterus, which is unacceptable for a nulliparous girl, since it can cause further unwanted pregnancy complications and even provoke a miscarriage. Of course, in a woman who has given birth before, such manifestations are also undesirable, but her body is protected in a certain way due to the acquired immunity.
In any case, the answer to the question whether it is possible to cauterize erosion for nulliparous women is categorically negative. Among the reasons are possible difficulties with further pregnancy, destabilization of hormonal levels, scarring of the epithelial tissues of the inner surface of the uterine cervix.

Among the possible consequences when using the cauterization method, it is worth noting such phenomena as:
- the formation of scars and scars on the epithelial tissue of the uterine cavity;
- uterine bleeding and increased risk of miscarriage;
- infertility.
Thus, for cervical erosion, being treated with cauterization is not only ineffective, but also dangerous to health.
In addition, modern medicine offers a wide range of effective alternative methods to avoid unwanted interference in the vital functions of the female body.
Drug therapy: application possibilities
Cervical erosion is a rather complex disease that requires an integrated approach to treatment. Many specialists are actively working to create innovative methods for the treatment of erosive pathologies of the uterine cavity, aimed at minimizing the negative side effects of the course of treatment.
In general, a set of therapeutic measures of a medicinal nature is aimed at eliminating the inflammatory process, combating the cause of inflammation and eliminating the possible consequences of the disease. In addition, special agents are used in the treatment to stimulate accelerated restoration of damaged tissues.

Treatment of cervical erosion in nulliparous women is based on the effective use of medications of different directions of action.
If cervical erosion is of infectious origin, treatment uses special agents that inhibit the action of pathogenic microorganisms that cause the infectious lesion.
Today, a gynecologist, instead of simply cauterizing the erosion, is obliged to examine the nature and dynamics of the disease, identify possible complications and make a clinical prognosis for rehabilitation.
In most cases, doctors simply reject radical methods of eliminating the disease as aggressive and detrimental to the quality of life and health of a woman. And, first of all, this concerns reproductive function.
For cervical erosion, nulliparous women are advised to strengthen the local component of treatment of the disease - through the use of appropriate ointments, gynecological suppositories and solutions. Of course, all medications must be agreed upon with the treating physician.
However, the course of treatment should be designed in such a way as to minimize symptoms, identify and eliminate the cause of the disease, and also promote the regeneration of cells damaged by erosion in the shortest period of time. The sooner the cause of the disease is identified and eliminated, the less harm is done to the woman’s reproductive system.

If you want to be cured of erosion and have a successful birth in the future, you should be very careful about following the prescriptions of drug therapy. In most cases, not only the dosage of the drug matters, but also the form of use, regularity and the combination of several medicinal formulas.
In the treatment of erosion, local agents are often used, which, when applied, promote atrophy of the affected tissue areas and the death of “sick” cells. The action of these drugs includes chemical coagulation - they are quite effective in localizing the symptoms that worry the patient and stopping foci of inflammation.
Among such medications are the drugs Solkovagin and Vagotil. The use of these drugs is strictly dosed - the treatment of damaged areas of epithelial uterine tissue is carried out directly by a gynecologist in a medical office.